Raymarching, voxelisation et visualisation musicale
- Motivation
- (R)appel: raymarching
- Raymarching voxélisé
- Post-traitements
- Visualisation musicale en shadertoy
- Démo
Motivation
Clips musicaux en stop motion:
Grindin' (Nobody Beats The Drum)
With Every Heartbeat (Robyn)
Brain (Étienne de Crécy)
8-bit trip, Brainglass, Kallbrand inst (Rymdreglagle)
Shaders et voxels:
Voxel Tyre (Dave Hoskins/ shadertoy)
Minecraft (Reinder Nijhoff / shadertoy)
Lego Castle (Antonalog / shadertoy)
Motivation
Shaders et musique:
Input - Sound (Íñigo Quílez / shadertoy)
Exemples: shadertoy [Soundcloud]
Visualisation musicale live:
Compétition: Revision 2014-2017 [Shader Showdown]
Compétition: Solskogen 2016-2017 [Live shader coding compo]
Logiciel de live coding musical: Bonzomatic
(R)appel: Algorithme de Raymarching
Raycasting:
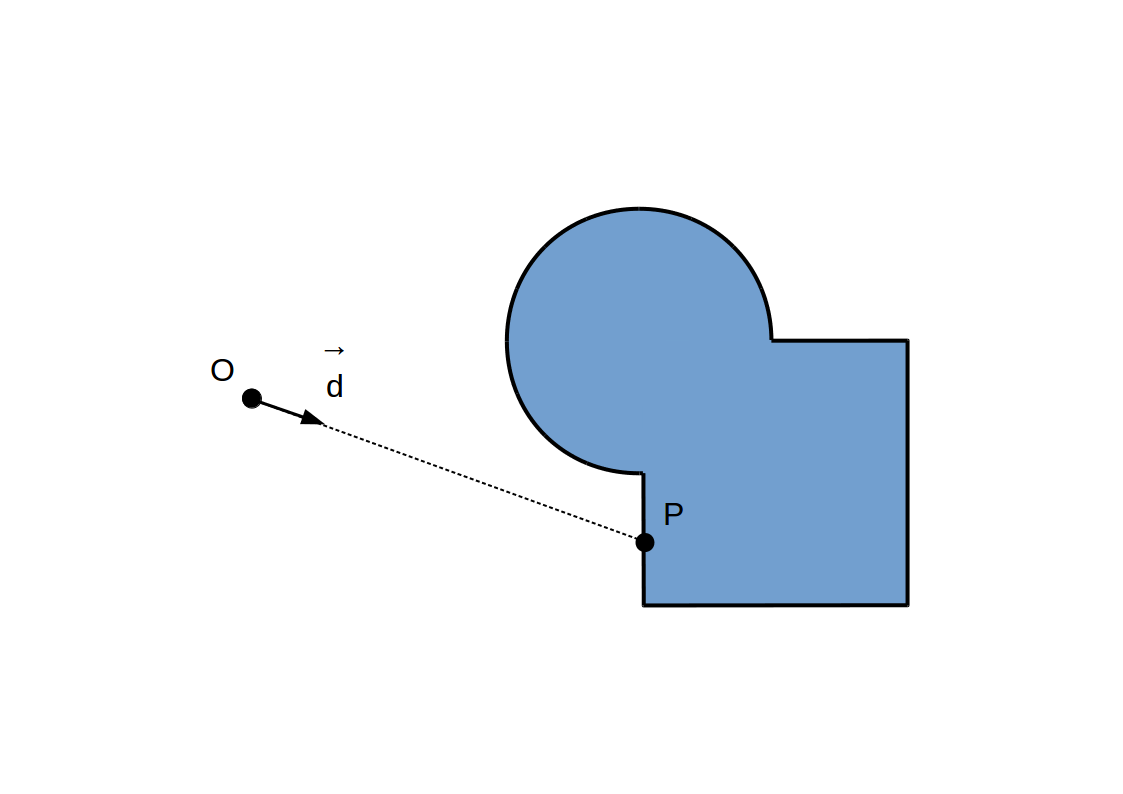
Raymarching à pas constant:
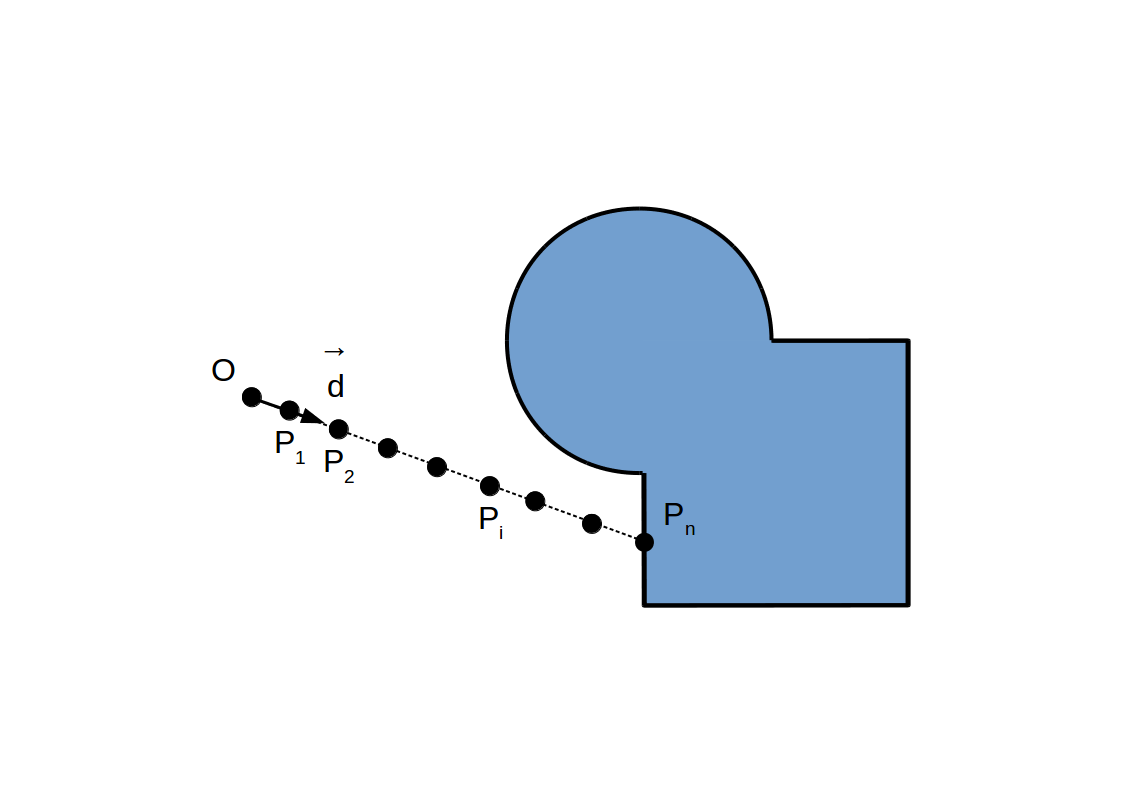
Raymarching à pas adaptif:
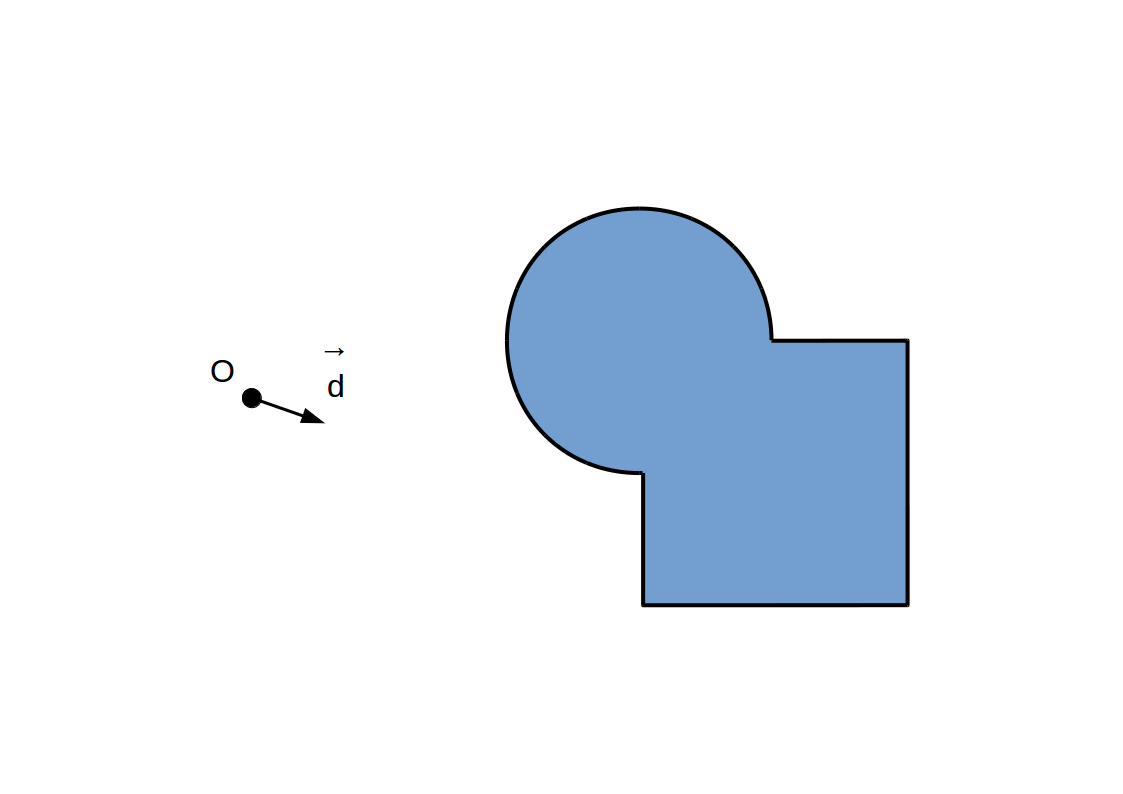
Raymarching à pas adaptif:
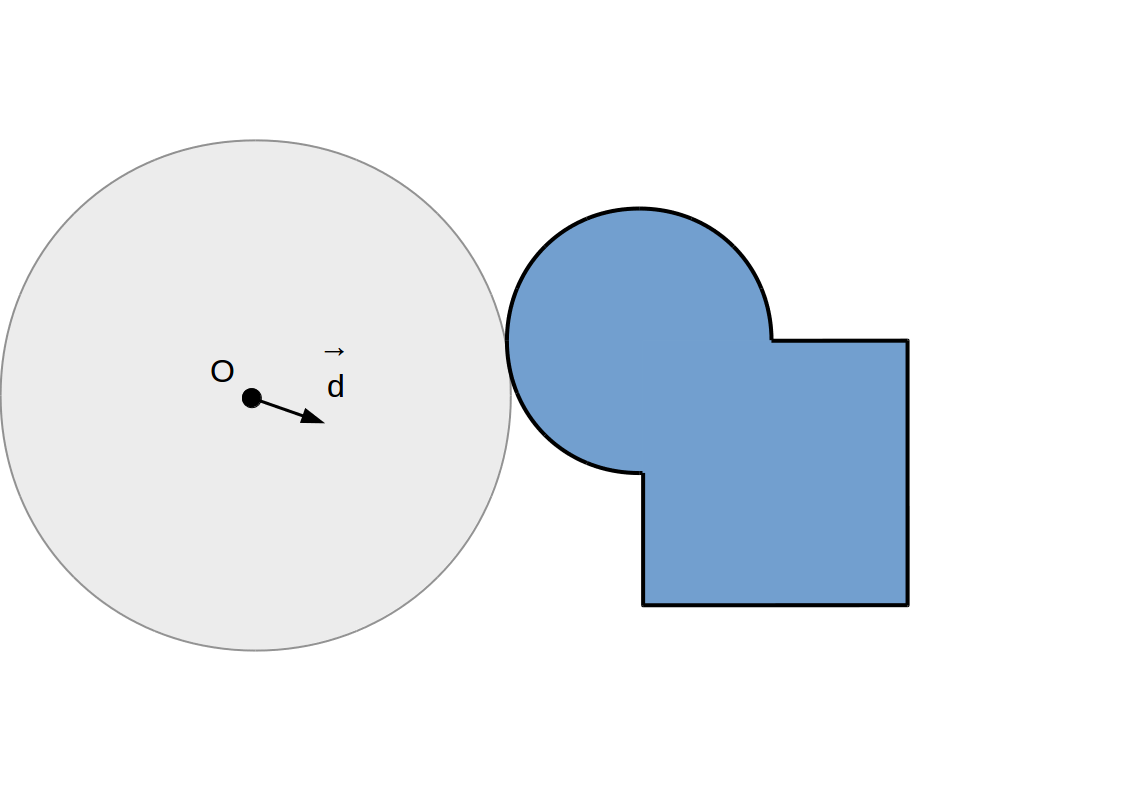
Raymarching à pas adaptif:
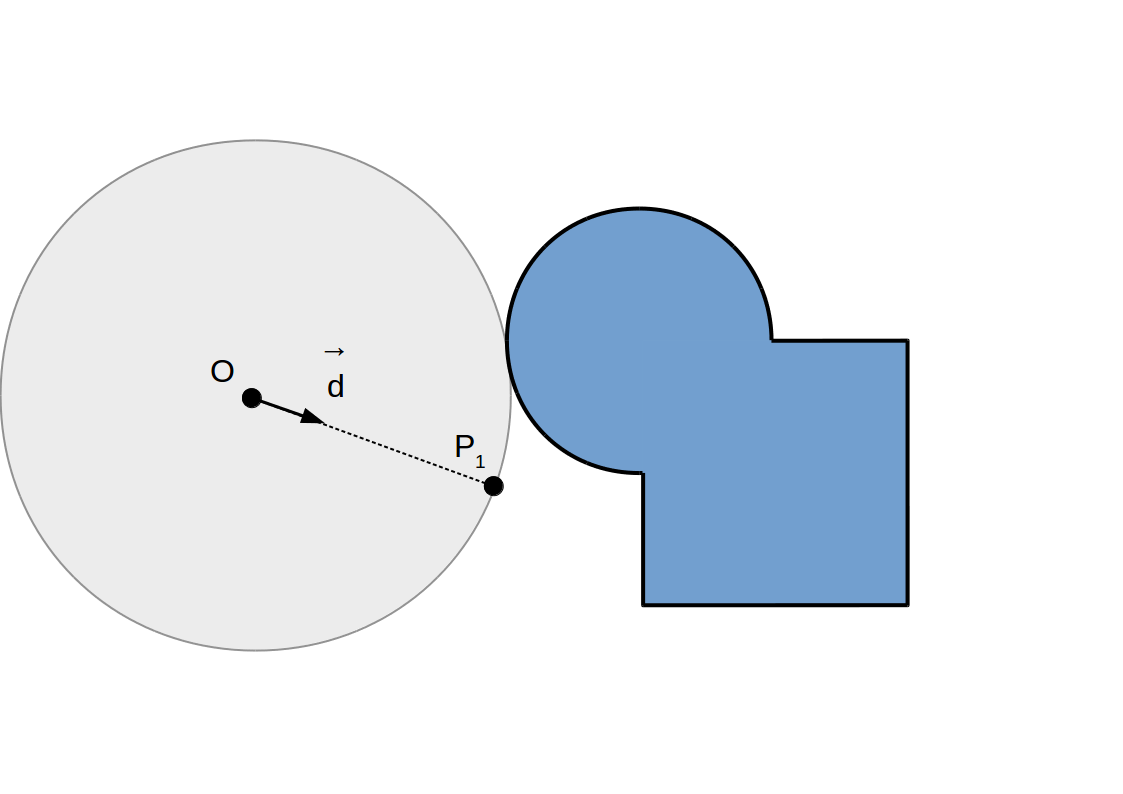
Raymarching à pas adaptif:
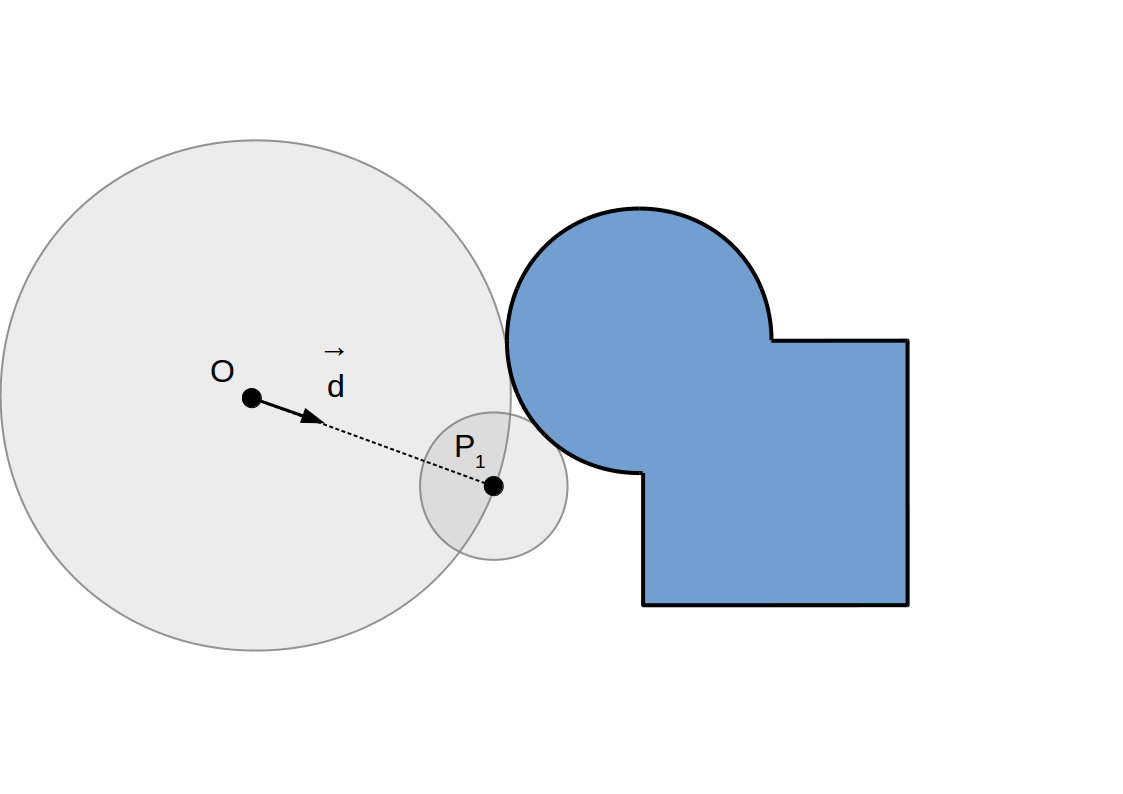
Raymarching à pas adaptif:
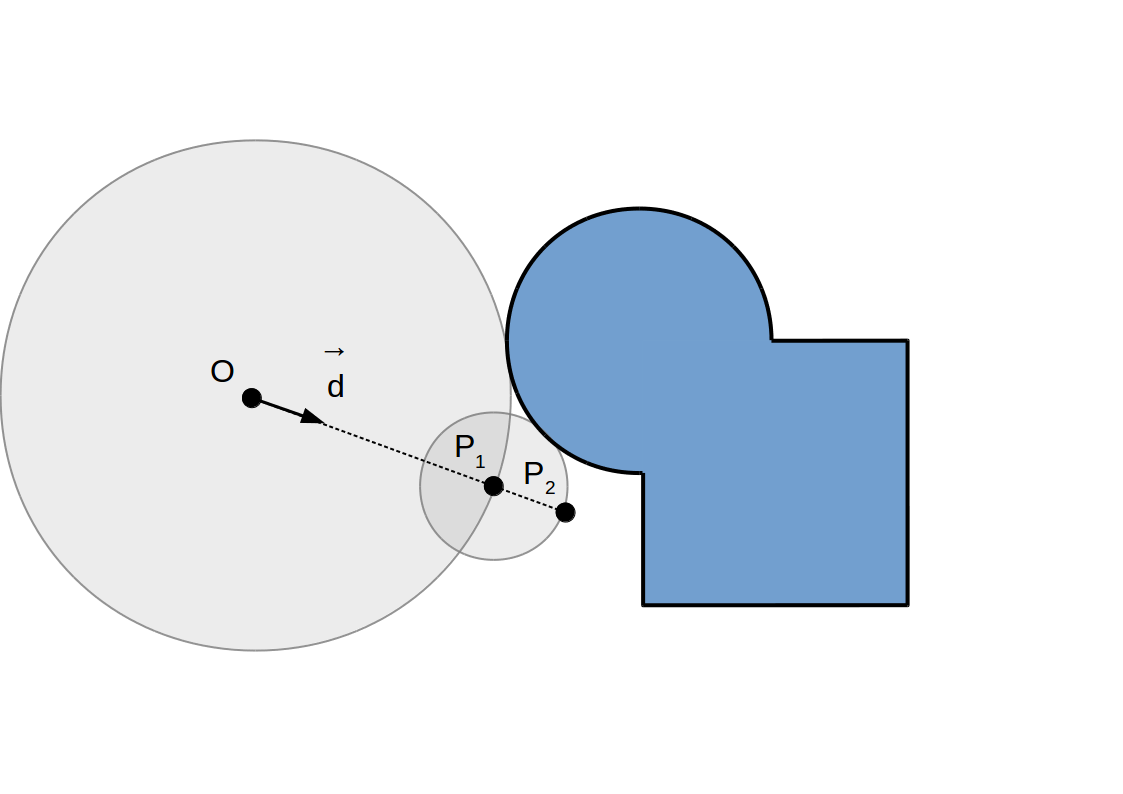
Raymarching à pas adaptif:
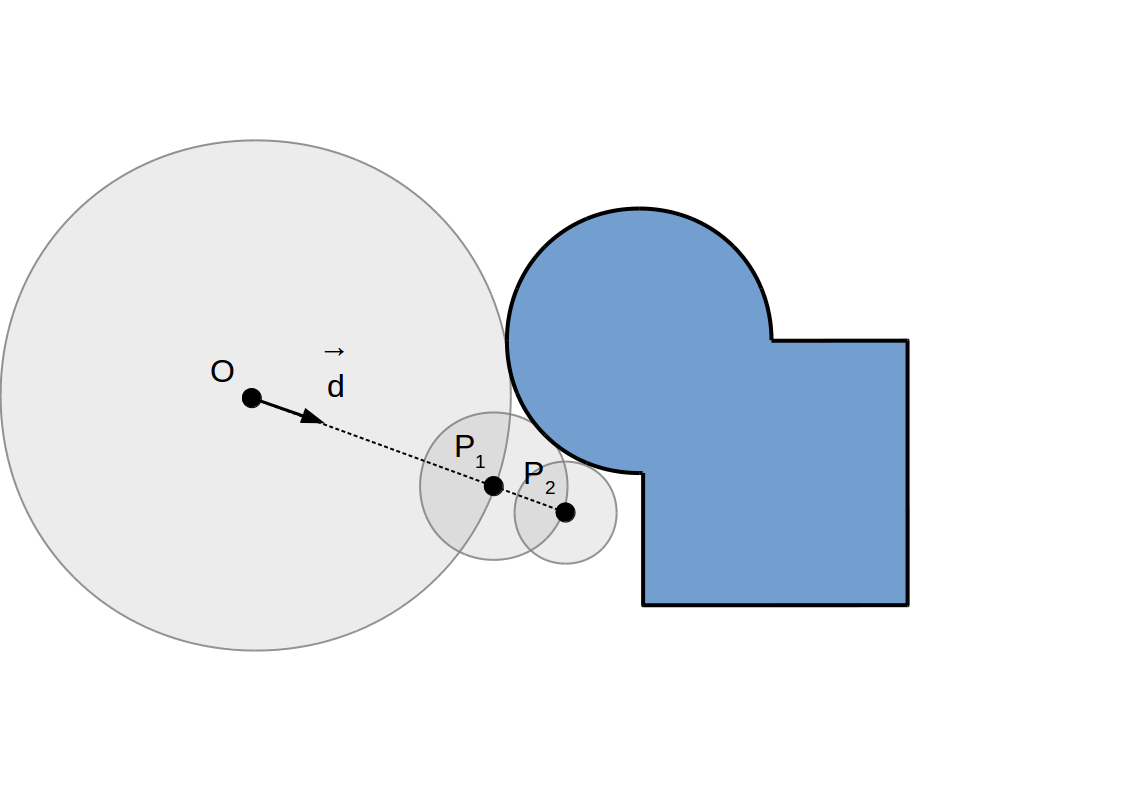
Raymarching à pas adaptif:
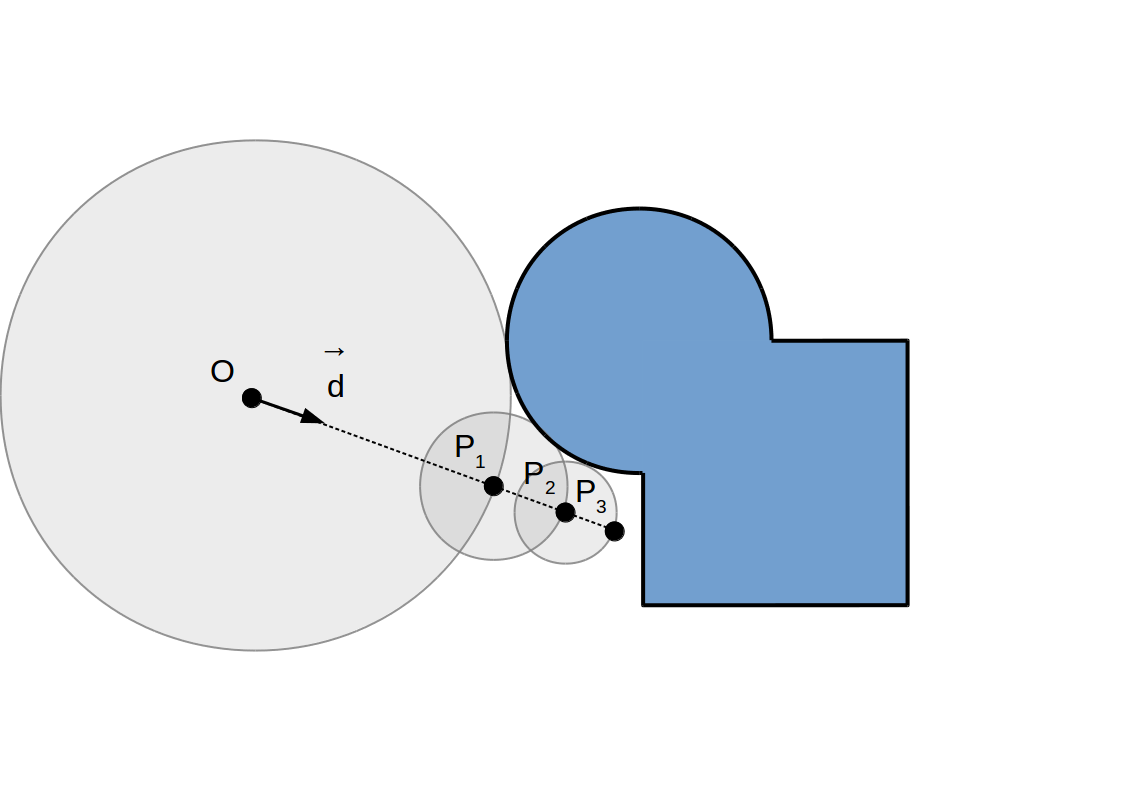
Raymarching à pas adaptif:
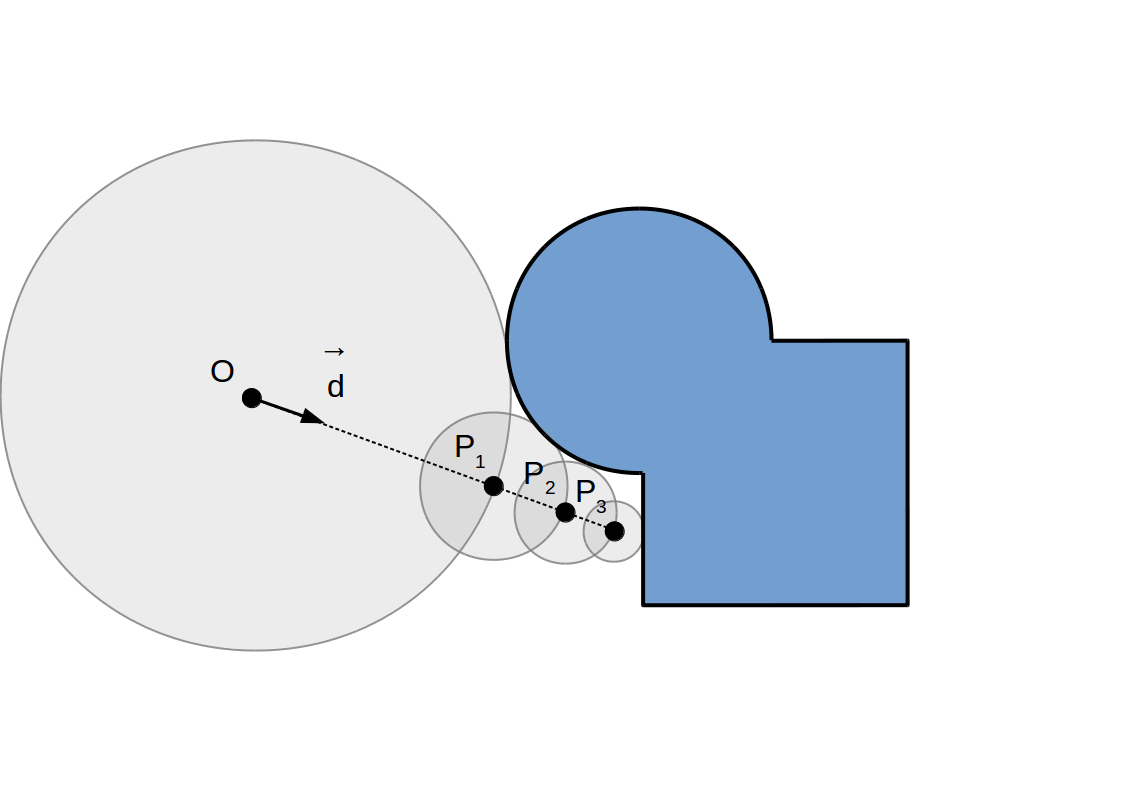
Raymarching à pas adaptif:
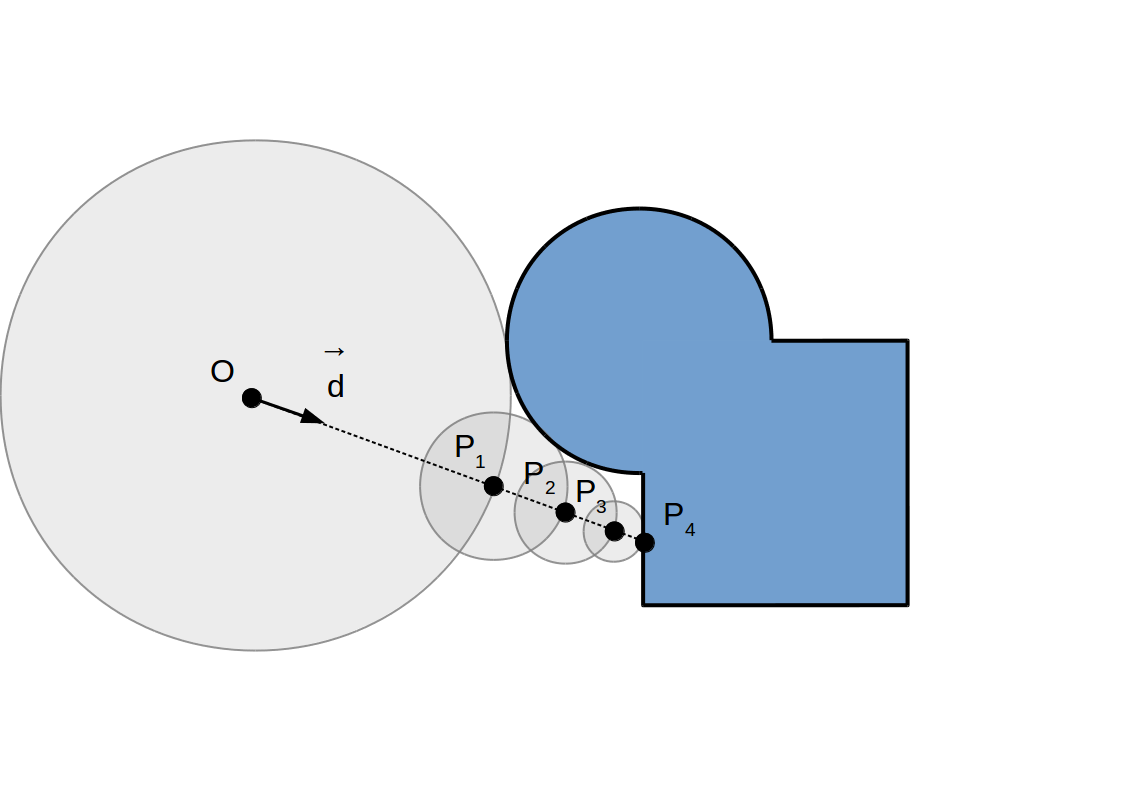
Raymarching à pas adaptif:
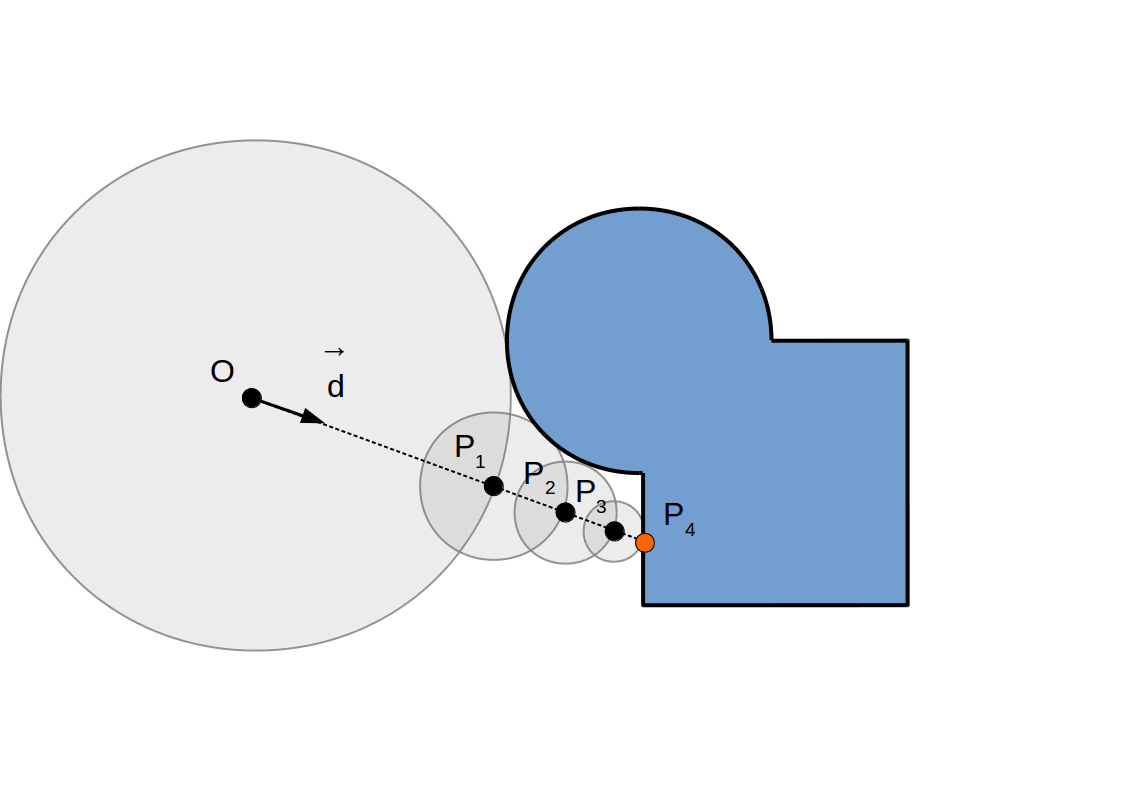
(R)appel: Implémentation
Code GLSL
float intersect(vec3 O /* origin */, vec3 d /* direction */) {
float t = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < MaxNumSteps; ++i) {
vec3 P = O + t * d;
float r = f(P);
if (r < Epsilon)
return t;
t += r;
}
return MaxT;
}
f(P)?
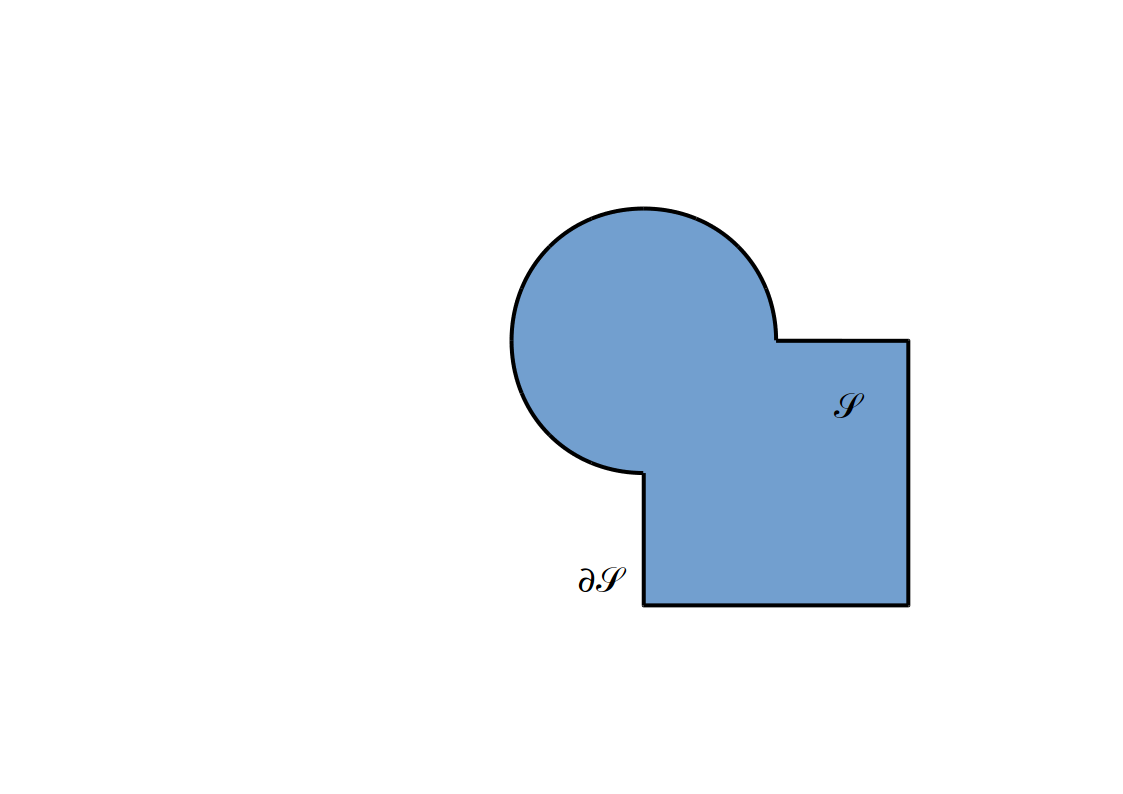
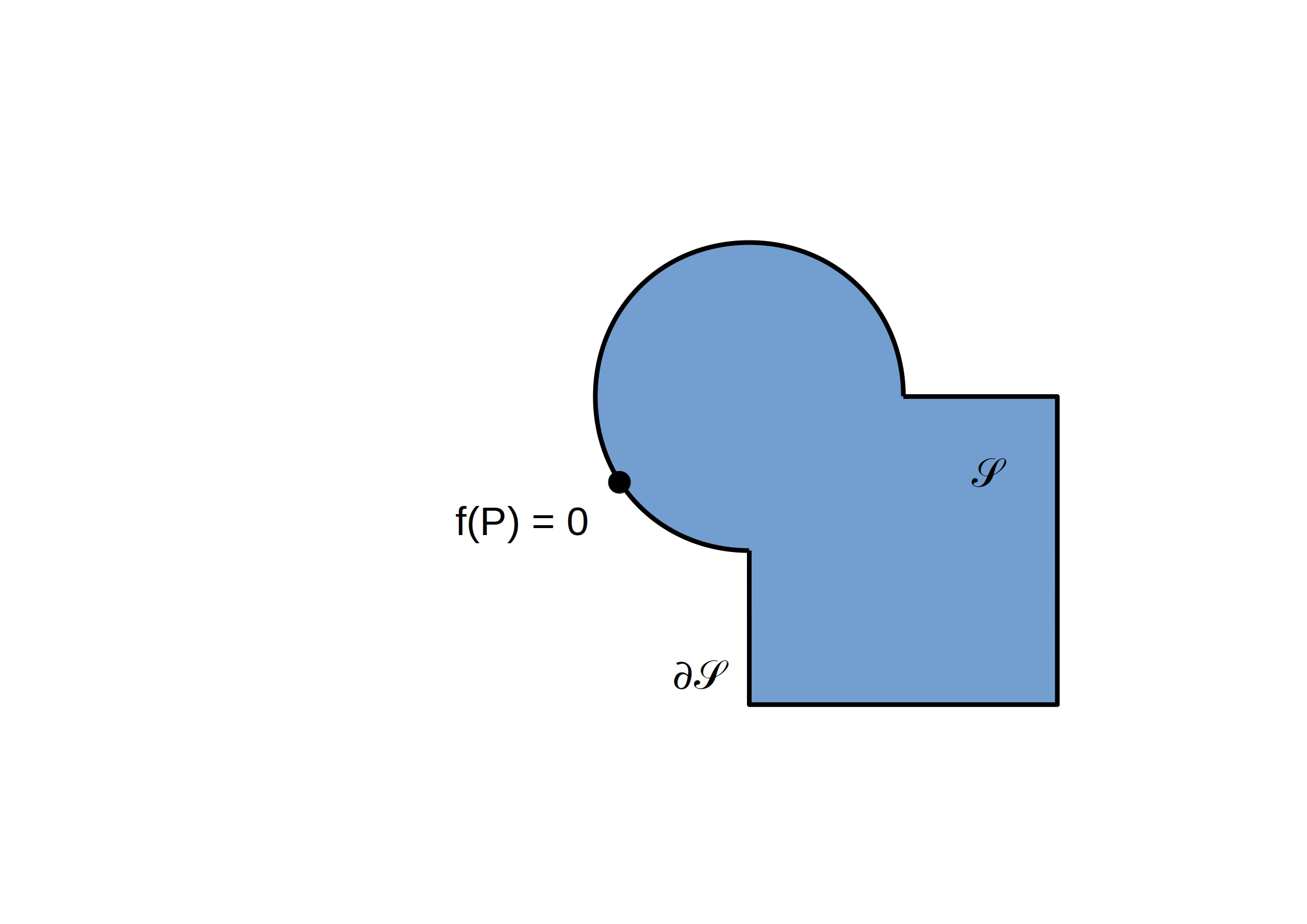
(R)appel: Fonction distance signée
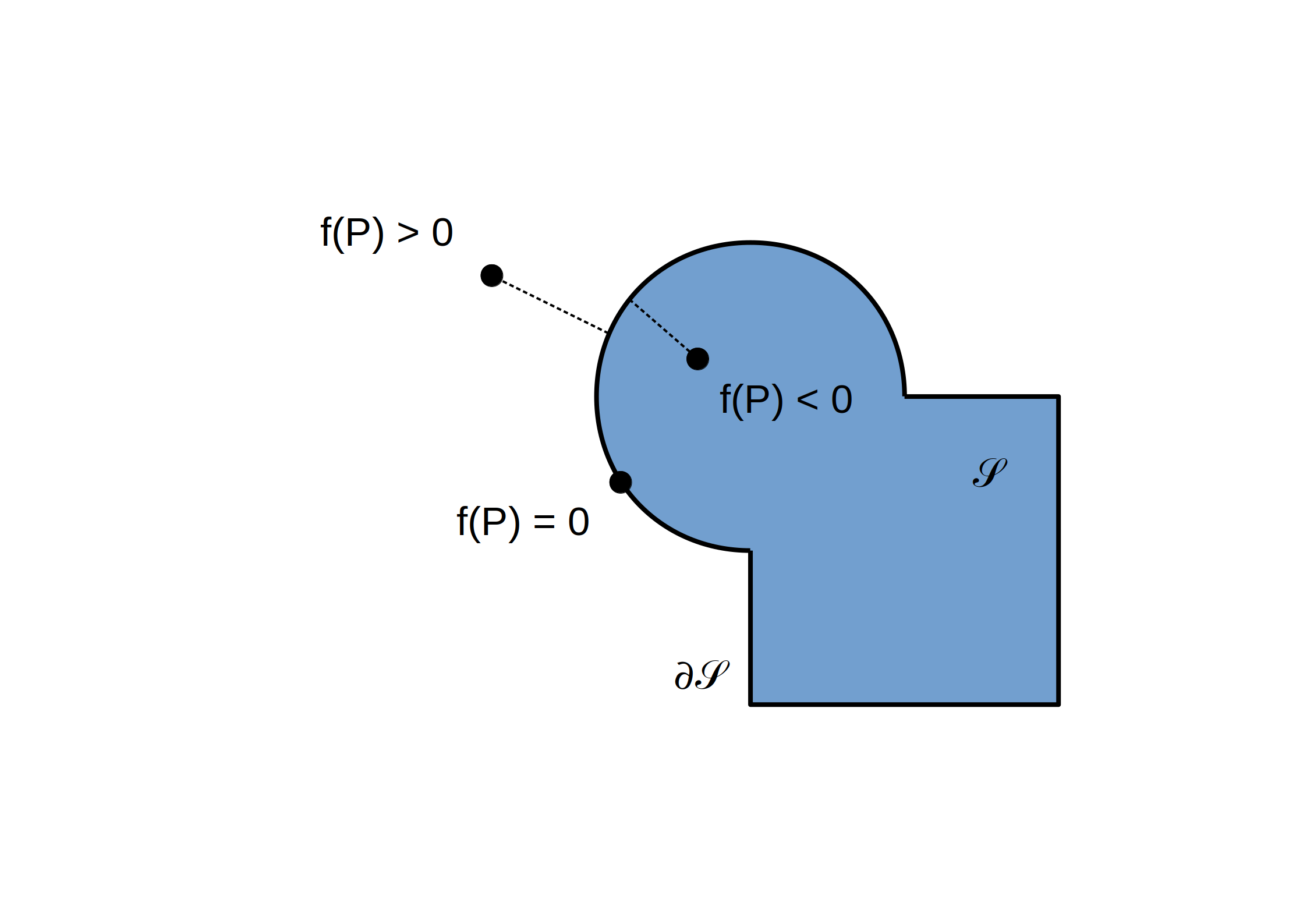
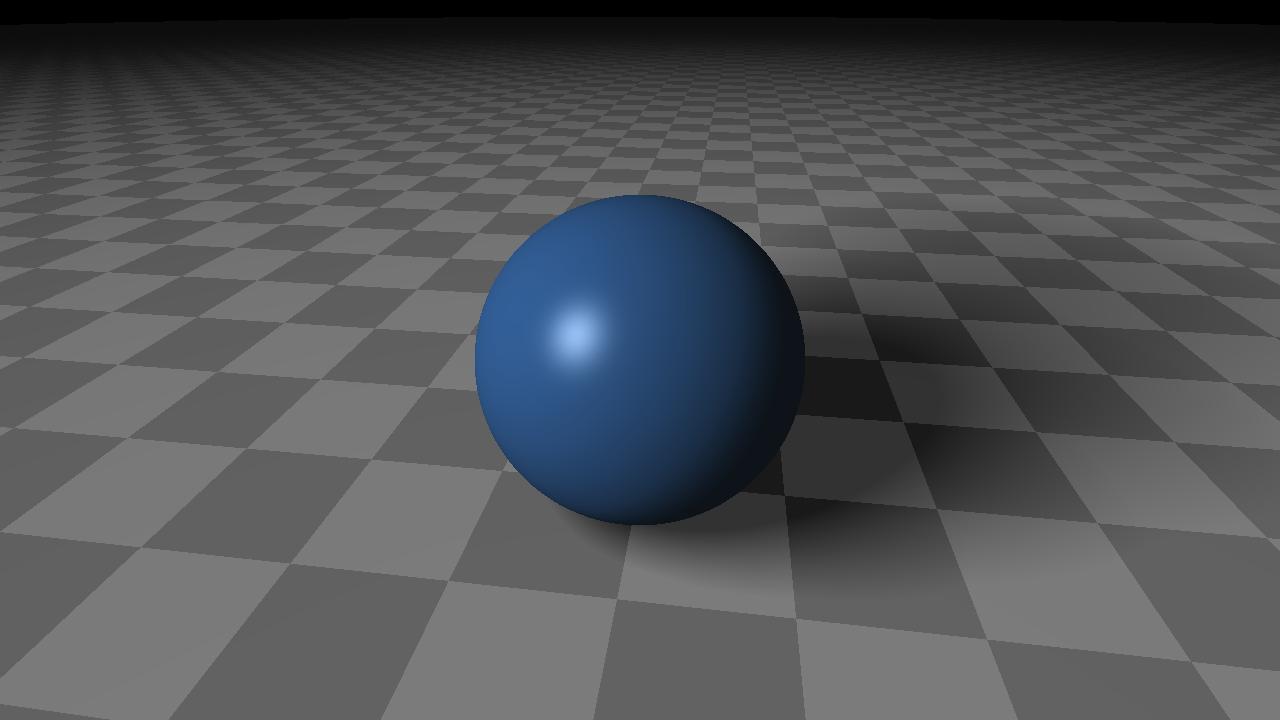
(R)appel: Primitives de base - Sphère
- Sphère
- centre `O`
- rayon `R`
- `f(P) = |vec(OP)| - R`
Code GLSL
float sdfSphere(vec3 P, float R) {
return length(P) - R;
}
(R)appel: Primitives, opérations, déformations
Primitives de base: demi-espace (plan), cylindre, tore, cone, ...
Opérations booléennes: union, intersection, différence, négation,
Déformations: translation, rotation, homothétie, symmétrie,
Déformations: répétition,
Déformations: torsion et courbure,
Déformations: déplacement,
Déformations: interpolation.
(R)appel: exemple de dérivation
- Pavé droit à trous cylindriques
- Pavé droit à arêtes arrondies
- Translation
- Cylindre
- Cylindre à section carrée
- Translation
- Cylindre à section hexagonale
- Union de 3 cylindres
- Différence (lissée)
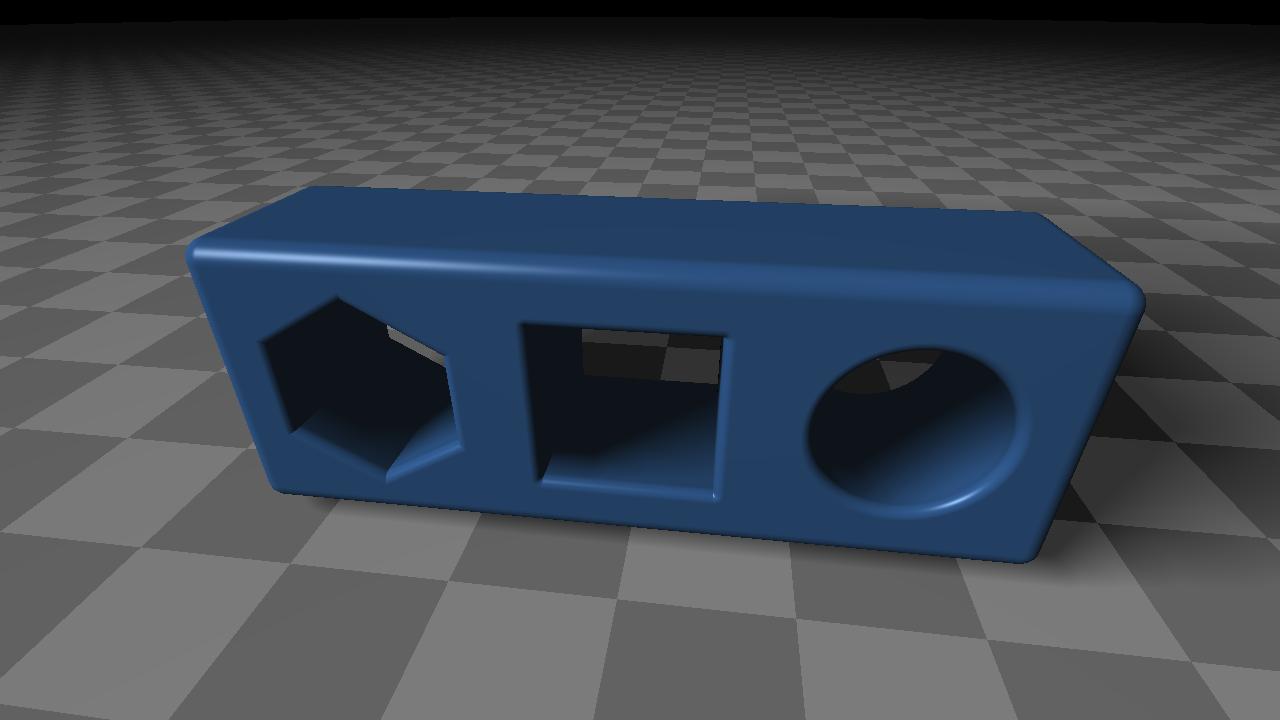
Code GLSL
float sdfBoxWithHoles(vec3 P) {
float d1 = sdfRoundBox(P, vec3(2.25, 0.75, 0.5), 0.125);
float d2 = sdfCylinder(P - vec3(1.5, 0.0, 0.0), 0.5);
float d3 = sdfBoxCylinder(P, vec2(0.5));
float d4 = sdfHexagonalCylinder(P + vec3(1.5, 0.0, 0.0), 0.5);
float d234 = min(d2, min(d3, d4));
vec2 u = max(vec2(0.0625 + d1, 0.0625 - d234), vec2(0.0));
return min(-0.0625, max(d1, -d234)) + length(u);
}
(R)appel: Illumination
Modèle de Phong:
`C_(p ixel) = C_(ambient) + C_(di f fuse) + C_(specu lar)`
`C_(ambient) = L_(ambient) M_(ambient)`
`C_(di f fuse) = L_(di f fuse) M_(di f fuse) max(< vec n . vec l >, 0)`
`C_(specu lar) = L_(specu lar) M_(specu lar) max(< vec r . vec l >, 0)^(shi ni n ess)`
La normale (sortante) `vec n` à `del ccS` est:
`vec n = vec grad f = ((del f) / (del x), (del f) / (del y), (del f) / (del z))`
Raymarching standard
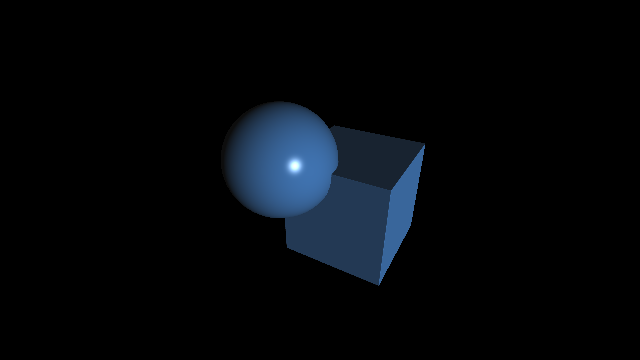
Code GLSL
float f(vec3 P) {
vec3 offset = 0.5 * vec3(-0.25, 0.25, 0.25);
float d1 = sdfSphere(P - offset, 0.25);
float d2 = sdfBox(P + offset, 0.25);
return min(d1, d2);
}
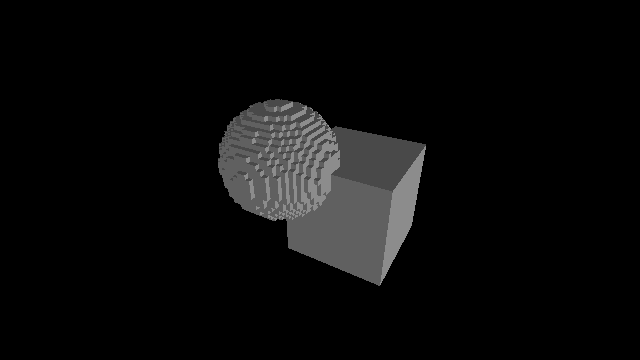
Raymarching voxélisé
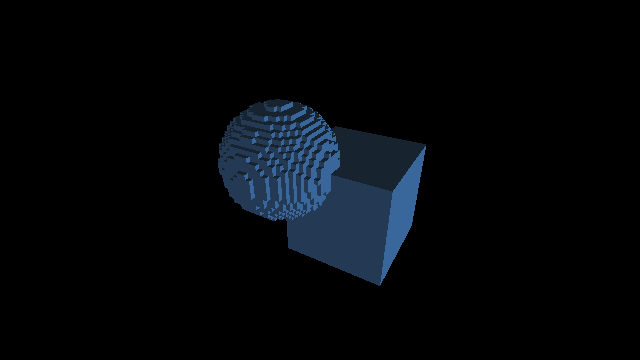
Code GLSL
float f(vec3 P) {
vec3 offset = 0.5 * vec3(-0.25, 0.25, 0.25);
float d1 = sdfSphere(P - offset, 0.25);
float d2 = sdfBox(P + offset, 0.25);
return min(d1, d2);
}
Raymarching voxélisé
Raymarching voxélisé:
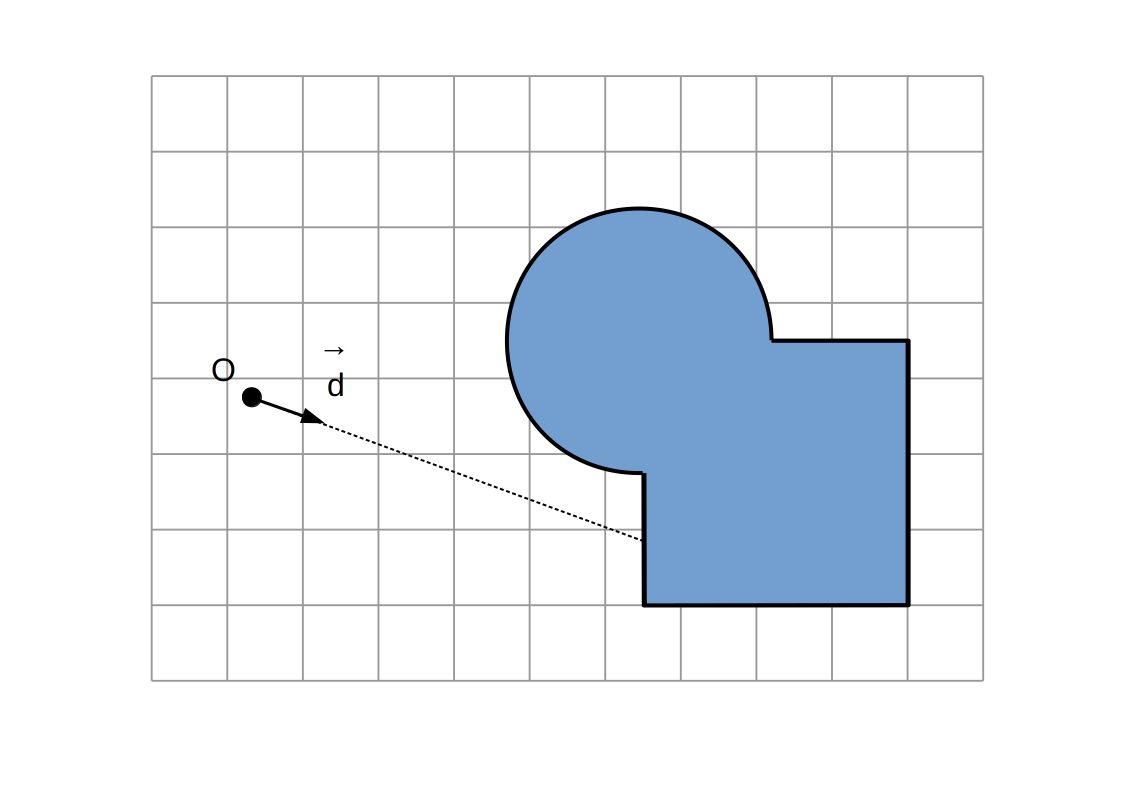
Raymarching voxélisé:
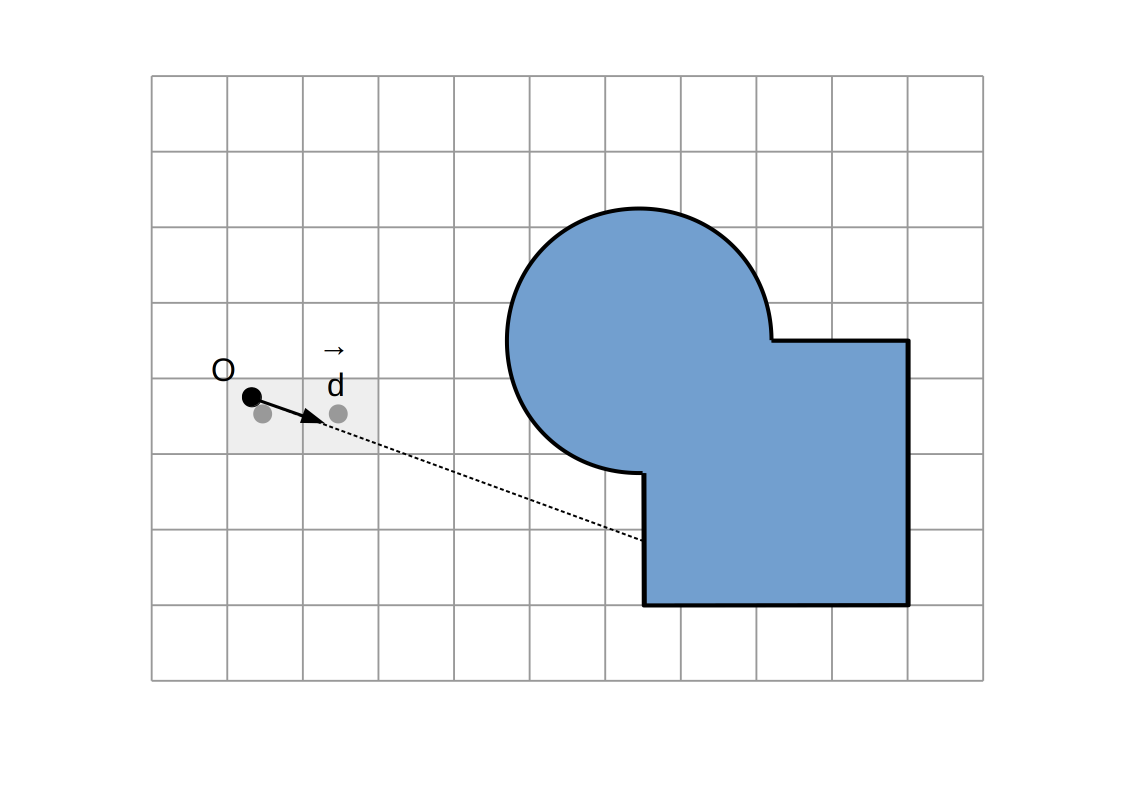
Raymarching voxélisé:
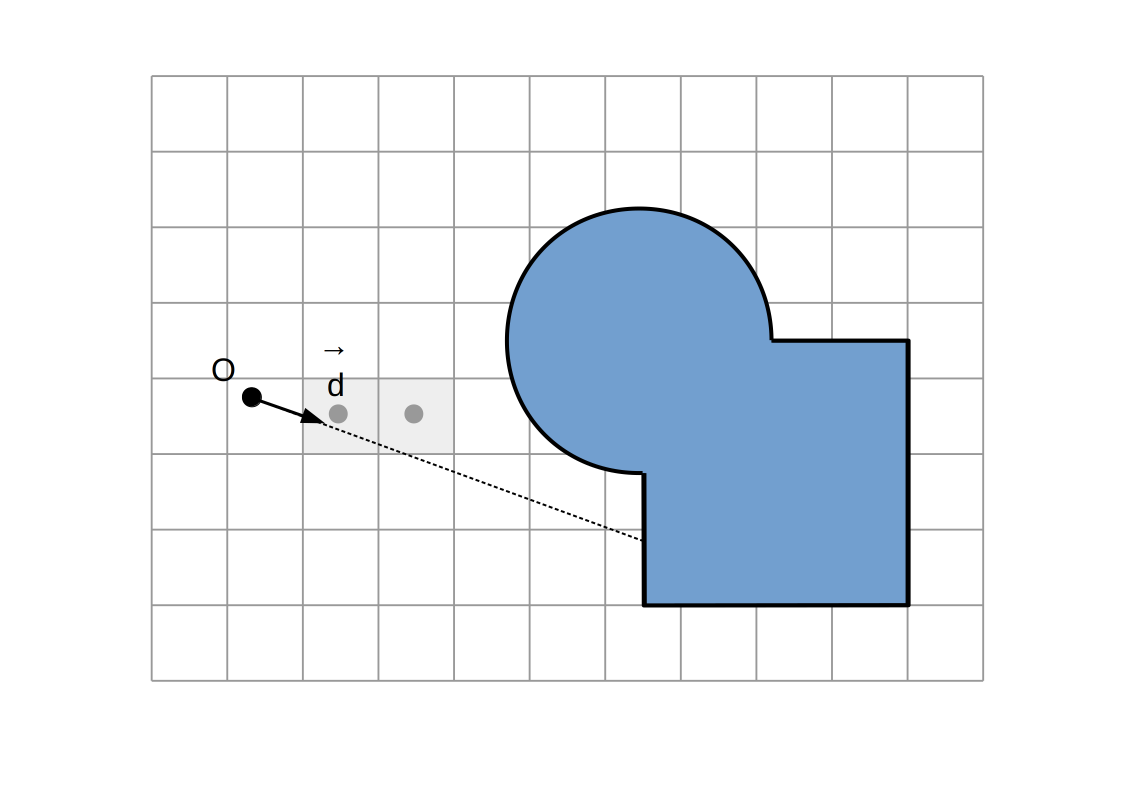
Raymarching voxélisé:
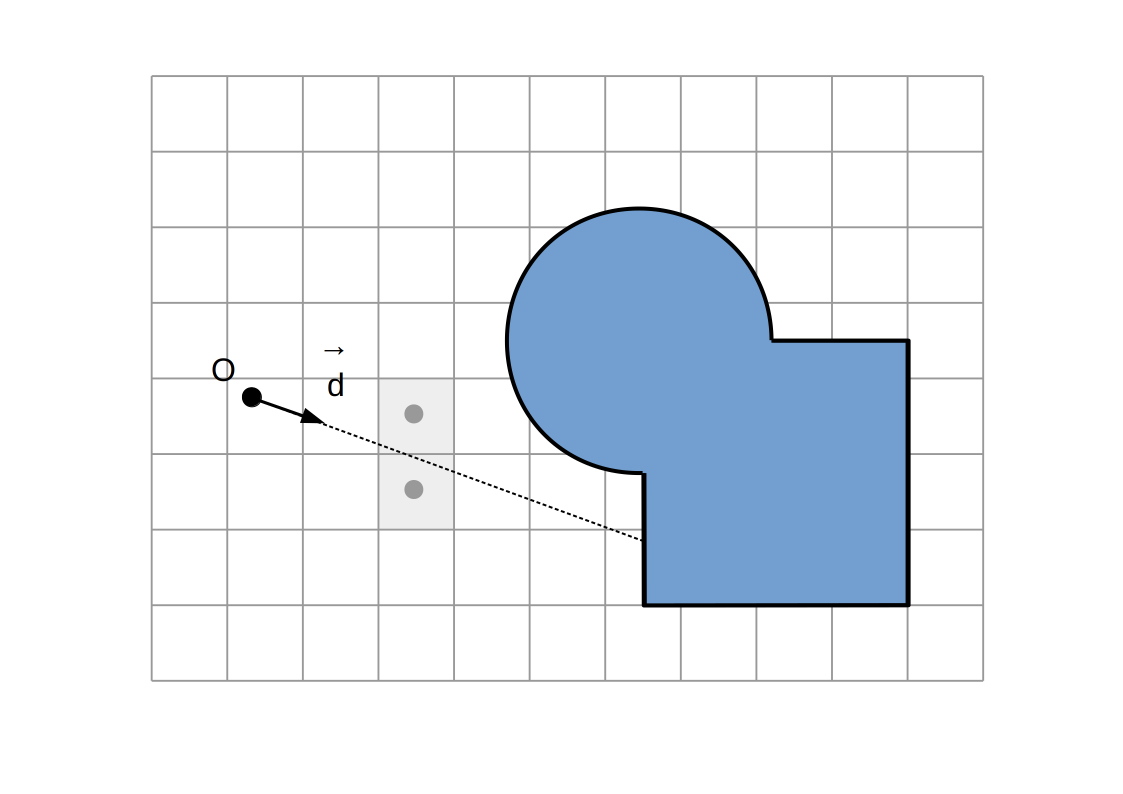
Raymarching voxélisé:
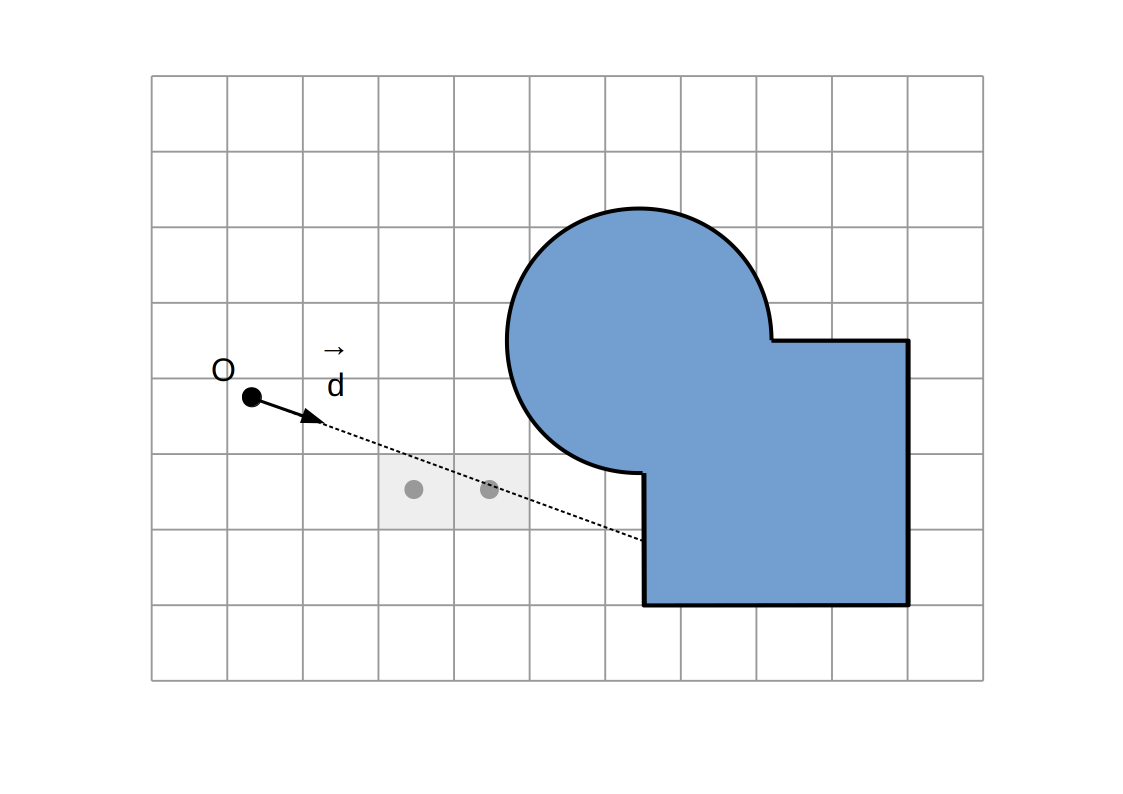
Raymarching voxélisé:
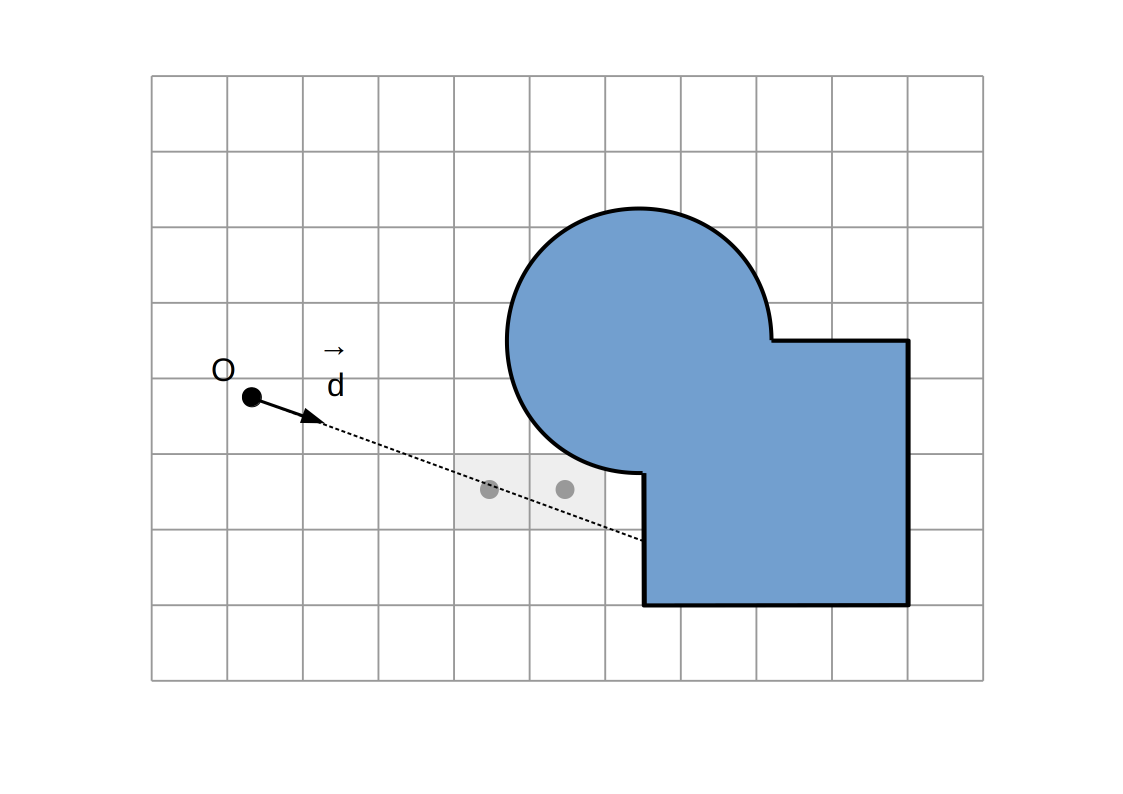
Raymarching voxélisé:
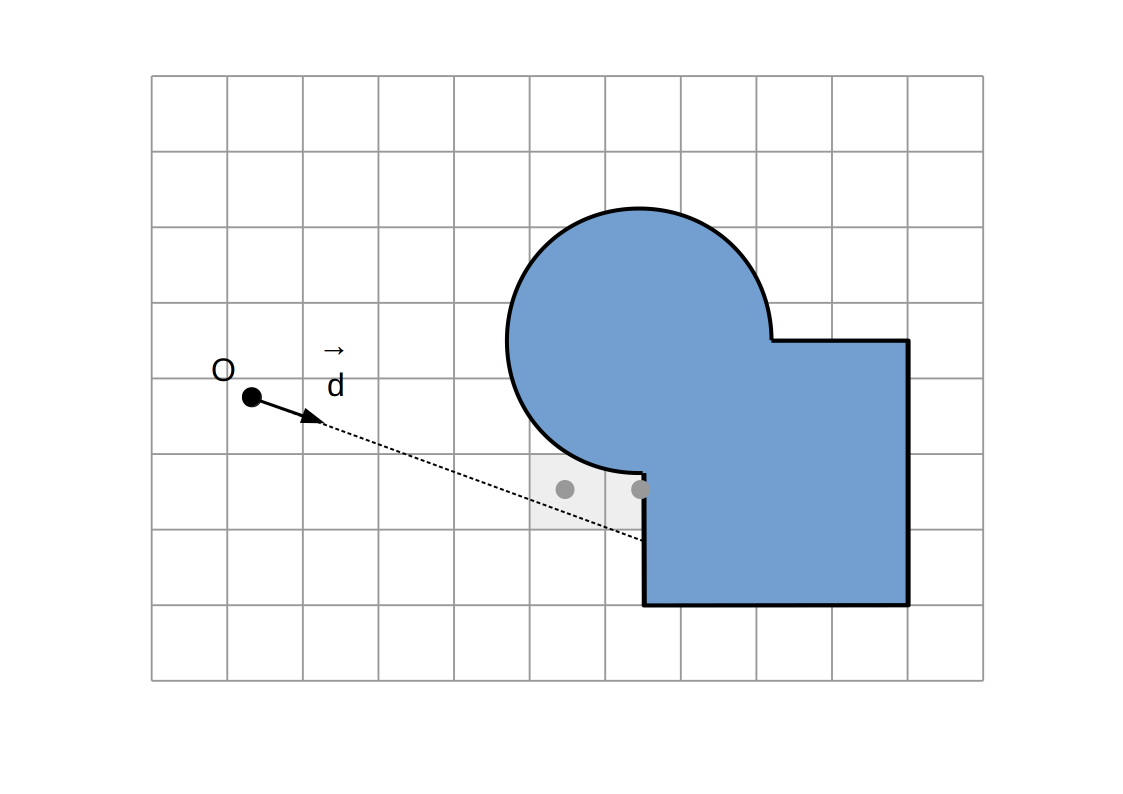
Raymarching voxélisé:
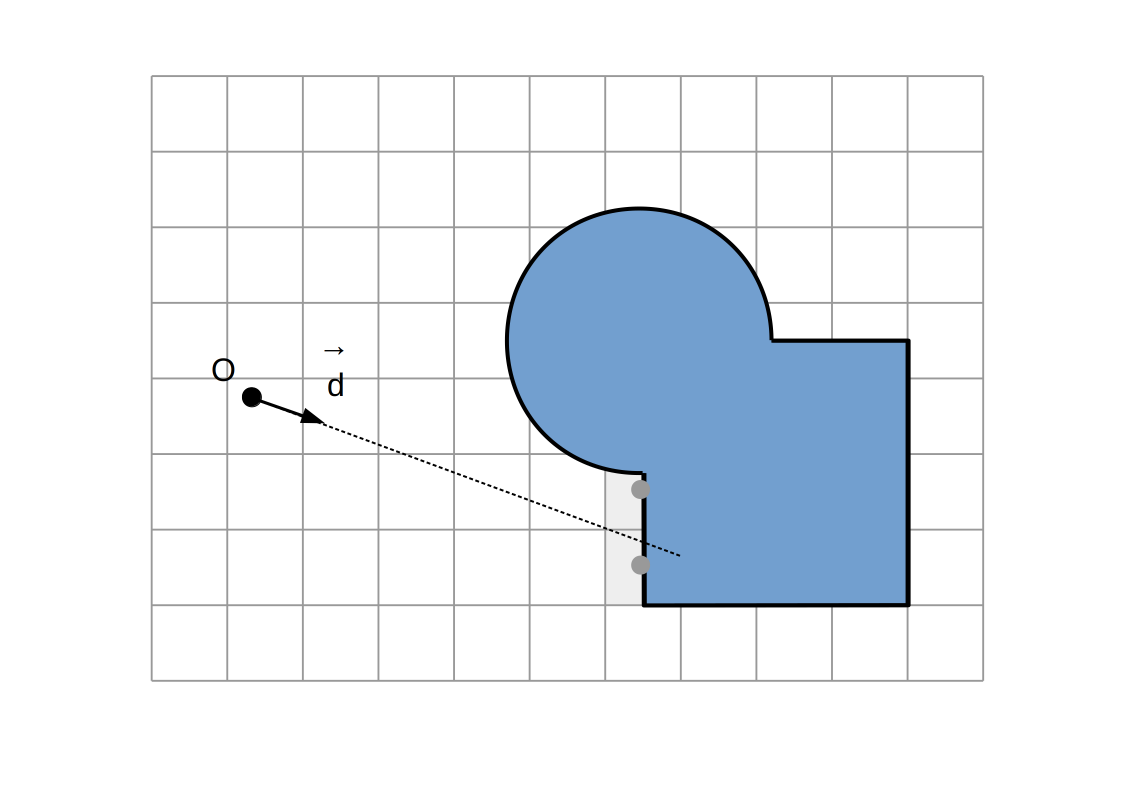
Raymarching voxélisé:
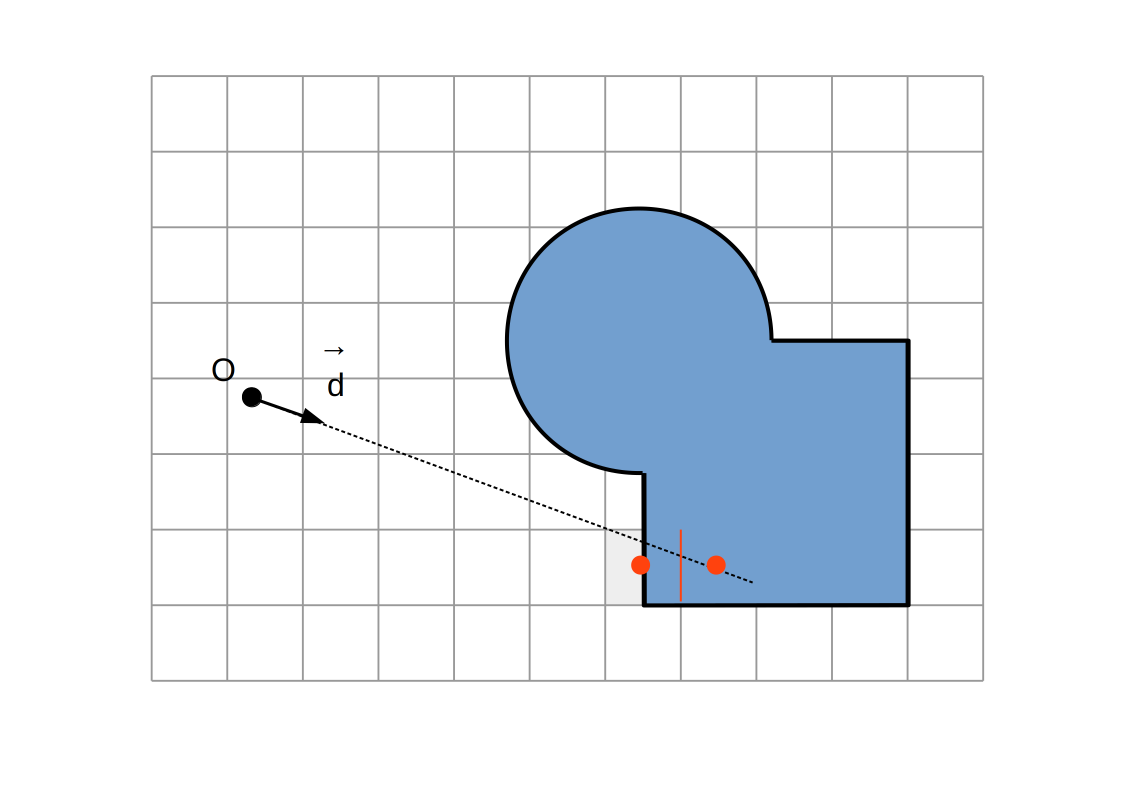
Raymarching voxélisé:
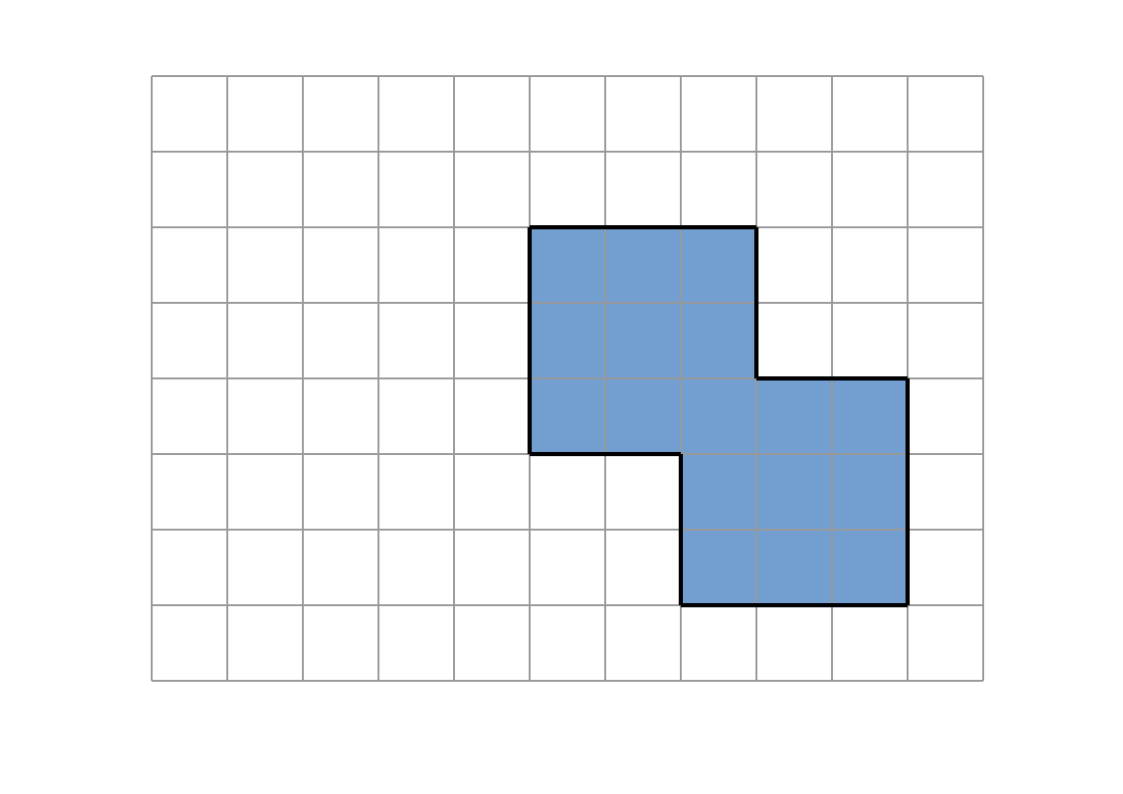
Raymarching voxélisé
Intersection `P`
Intersection du rayon `(O, vec d)` avec la dernière facette traversée
(ou milieu des centres des derniers voxels traversés)
Normale `vec n`
Direction `+-vec e_x`, `+-vec e_y`, `+-vec e_z` selon la dernière facette traversée et la direction du rayon
Aucune autre modification (calcul d'illumination, etc...)
Code GLSL
float intersectGrid(vec3 O, vec3 d, out vec3 n, float gridSize) {
// ...
}
Post-traitement: sans arêtes
Post-traitement: avec arêtes
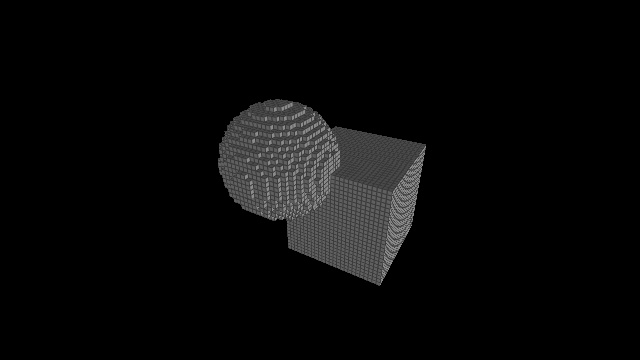
Post-traitement: détection d'arêtes
Code GLSL
float getEdgeFactor(vec3 P, float gridSize) {
const float EdgeHalfWidth = 0.15;
vec3 Q = abs(mod(P / vec3(gridSize) + 0.5, 1.0) - 0.5);
vec3 T = vec3(1.0) - smoothstep(vec3(0.0), vec3(EdgeHalfWidth), Q);
return max(T.x * T.y, max(T.y * T.z, T.z * T.x));
}
vec3 shade(vec3 O, vec3 P, vec3 n, vec3 l, float gridSize, ...) {
// ...
const vec3 EdgeColor = vec3(0.0625);
float a = getEdgeFactor(P, gridSize);
diffuse = mix(diffuse, EdgeColor, a);
return ambient + diffuse * max(dot(n, l), 0.0) + ...;
}
Arêtes internes / bord: Voxel lines and occlusion, Voxel Edges (Íñigo Quílez / shadertoy)
Post-traitement: occlusion ambiante
`C_(p ixel) = C_(ambient) + C_(di f fuse) + C_(specu lar)`
`C_(ambient) = L_(ambient) M_(ambient)`
Remplacer `L_(ambient)` (constante) par une valeur modulée par le degré d'occlusion de la géométrie locale de la scène.
En pratique:
- Échantillonner l'occlusion dans la direction de `vec n`,
- Pour chaque échantillon `Q`, l'occlusion est dérivée de `f(Q)`,
- [Voxélisation] Utiliser la distance à la surface voxélisée à la place de `f(Q)`.
Post-traitement: occlusion ambiante
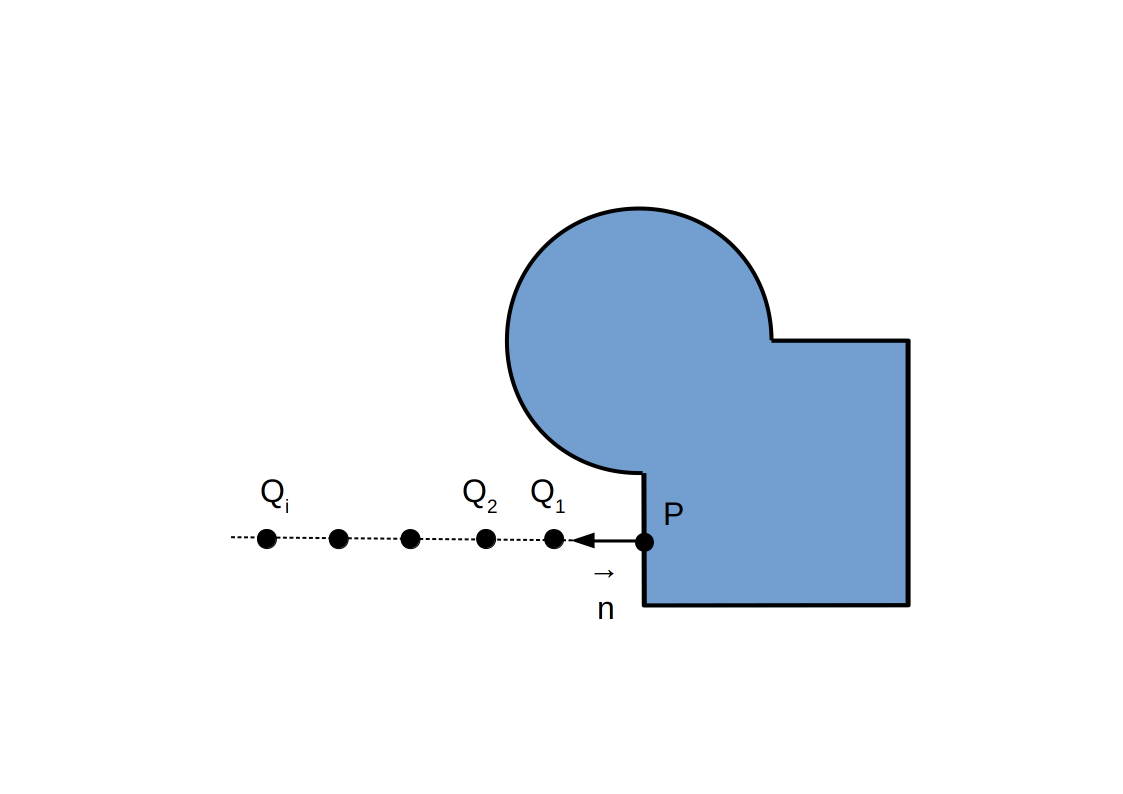
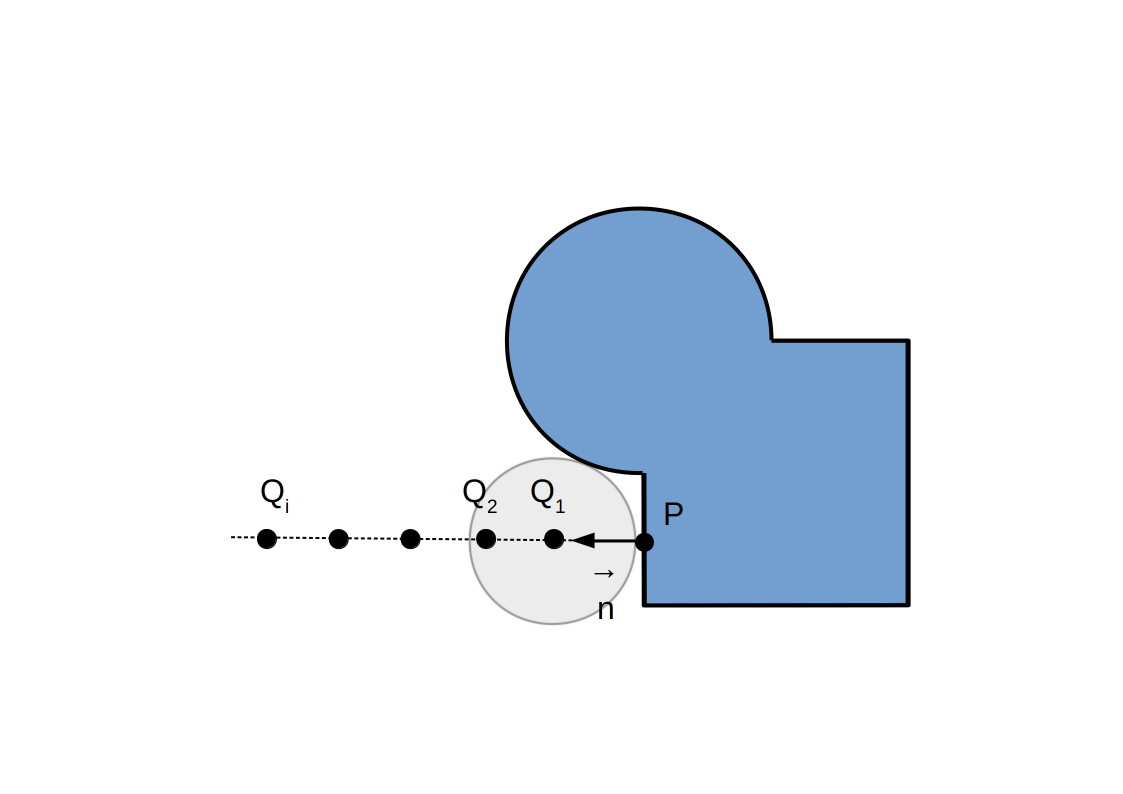
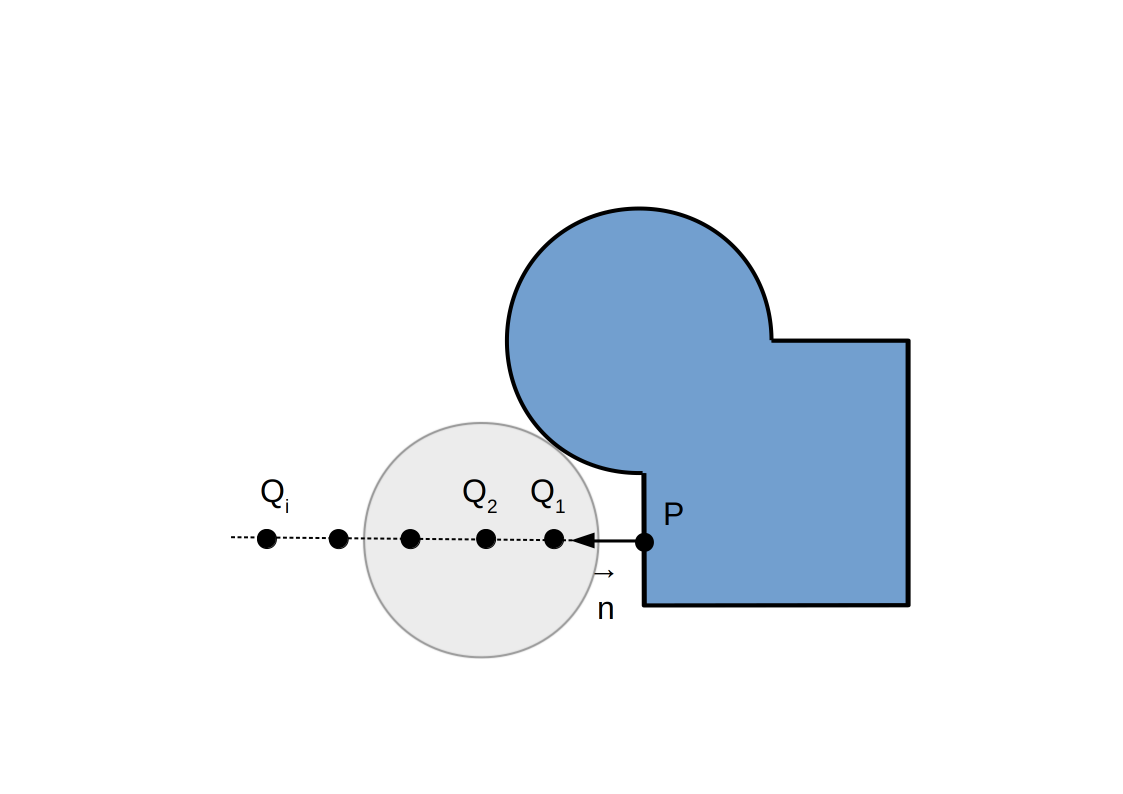
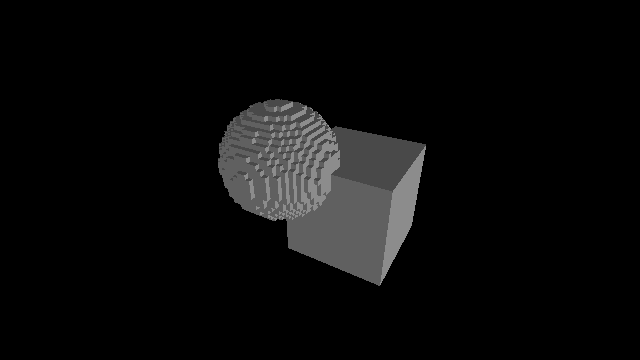
Post-traitement: sans occlusion ambiante
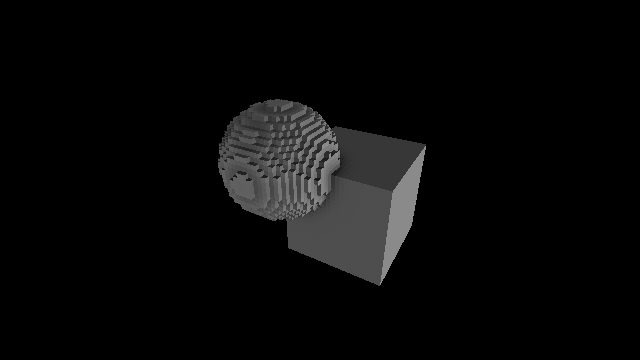
Post-traitement: avec occlusion ambiante
Post-traitement: occlusion ambiante
Code GLSL
float ambientOcclusion(vec3 P, vec3 n, float gridSize) {
float dt = 0.9 * gridSize;
float t = dt;
float ao = 0.0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; ++i) {
vec3 Q = P + t * n;
vec3 R = gridSize * (floor(Q / gridSize) + vec3(0.5));
ao += (t - f(R)) / pow(2.0, float(i));
t += dt;
}
return 1.0 - clamp(ao, 0.0, 1.0);
}
vec3 shade(vec3 O, vec3 P, vec3 n, vec3 l, float gridSize, ...) {
float ao = ambientOcclusion(P, n, gridSize);
// ...
return ao * ambient + diffuse * max(dot(n, l), 0.0) + ...;
}
Visualisation musicale en shadertoy
- Sélectionner comme texture d'entrée (e.g.
iChannel0):- une des musiques prédéfinies,
- le microphone,
- un clip audio sur SoundCloud.
- Utiliser la texture dans le shader:
1ère ligne: spectre (magnitude normalisée de la FFT)
2ème ligne: échantillon de musique (mono canal normalisé)
Code GLSL
float fft = texture(iChannel0, vec2(f, 0.25)).x; // Spectre float wave = texture(iChannel0, vec2(t, 0.75)).x; // Échantillon
Visualisation musicale en shadertoy
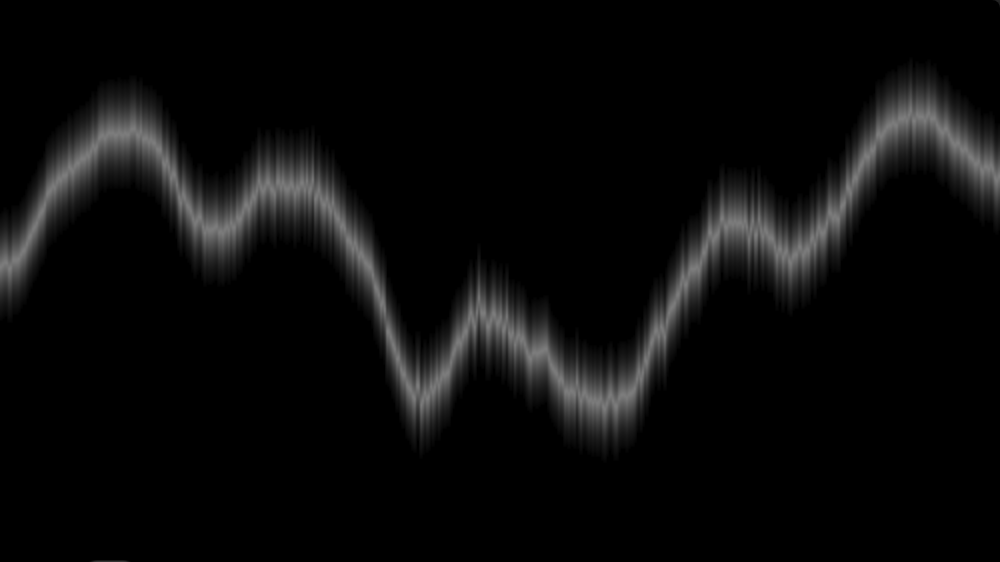
Code GLSL
void mainImage(out vec4 fragColor, in vec2 fragCoord) {
vec2 uv = fragCoord.xy / iResolution.xy;
float wave = texture(iChannel0, vec2(uv.x, 0.75)).x;
vec3 color = vec3(1.0 - smoothstep(-0.1, 0.1, abs(wave - uv.y)));
fragColor = vec4(color, 1.0);
}
Visualisation musicale en shadertoy
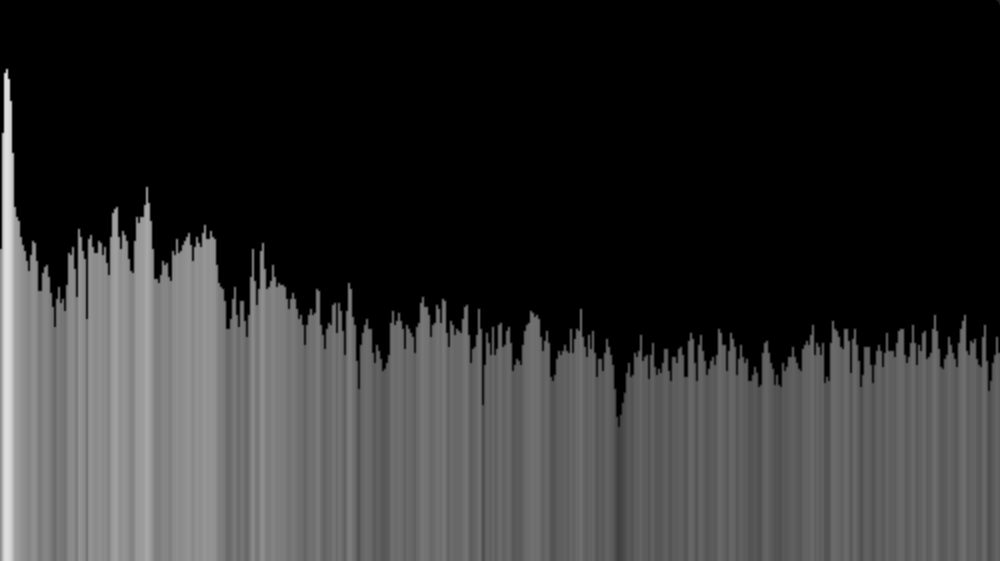
Code GLSL
void mainImage(out vec4 fragColor, in vec2 fragCoord) {
vec2 uv = fragCoord.xy / iResolution.xy;
float fft = texture(iChannel0, vec2(uv.x, 0.25)).x;
vec3 color = vec3(fft > uv.y ? fft : 0.0);
fragColor = vec4(color, 1.0);
}
Démo