Rendu 3D (avec Processing)
- Exemples
- Introduction
- Caméra
- Géométrie
- Matériaux et Illumination
Exemples (Processing.js)
Watch your step (snowdrop42)
3D Gravity Well (Marvin K)
3D Arcs (Jerome Faria)
Form 333B (Raven Kwok)
Spiral Orbit Boxes (Patrick DiGiovanni)
Spirals (Tetsuya Matsuno)
Introduction
Rendu 2D
Code Processing
size(WIDTH, HEIGHT, P2D);
Rendu 3D
Code Processing
size(WIDTH, HEIGHT, P3D);
Système de coordonnées
- origine en haut à gauche,
- axe x (horizontal) croissant vers la droite,
- axe y (vertical) croissant vers le bas,
- axe z (profondeur) croissant vers l'écran.
Introduction
Opérations
Code Processing
PVector v = new PVector(x, y, z);
translate(tx, ty, tz);
rotateX(angle);
rotateY(angle);
rotateZ(angle);
scale(sx, sy, sz);
Primitives
Code Processing
point(x, y, z);
line(x1, y1, z1, x2, y2, z2);
box(width, height, depth);
sphere(radius);
Caméra
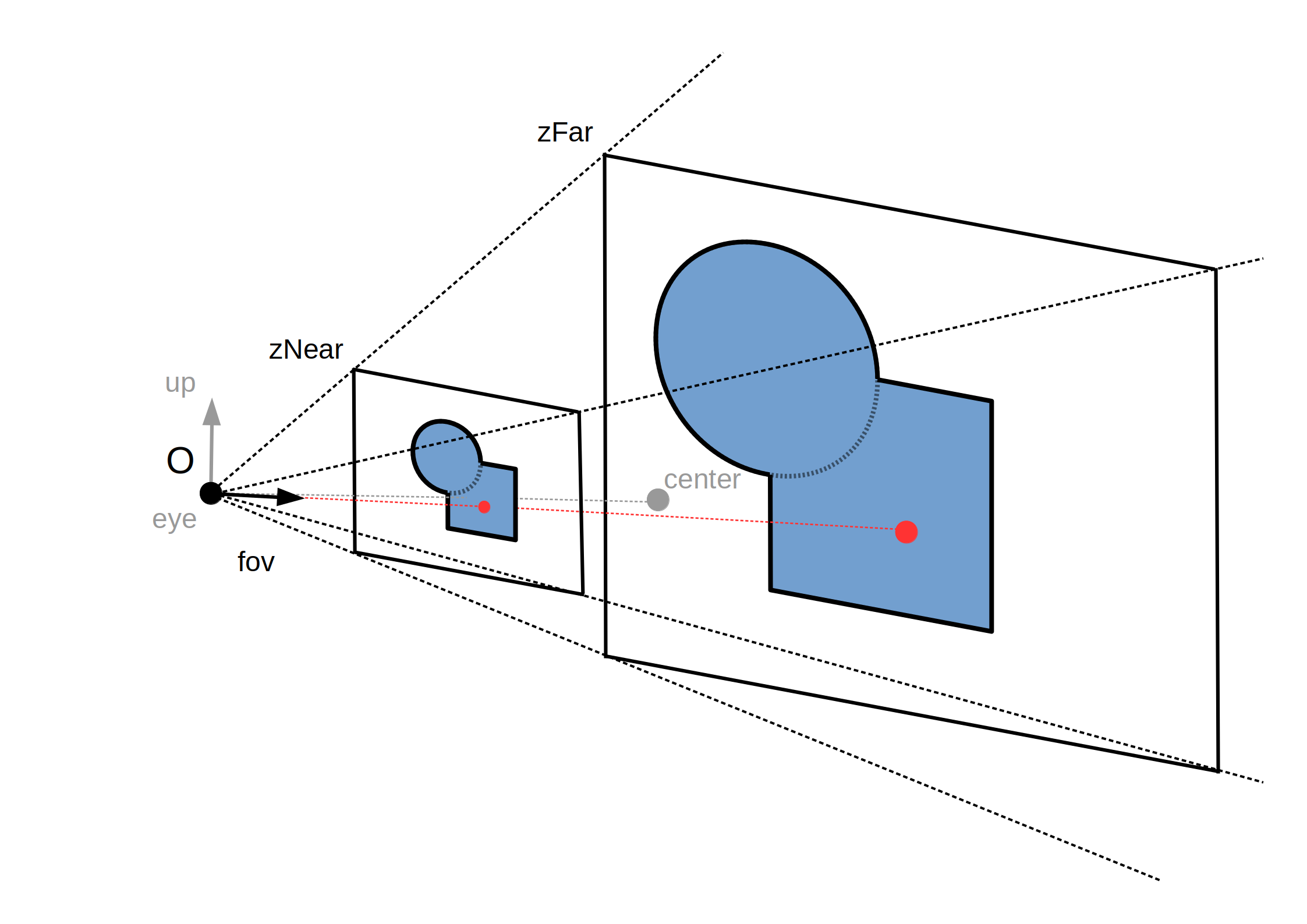
Caméra
Position: position de la caméra-oeil / du centre, vecteur vertical
Code Processing
camera(eyeX, eyeY, eyeZ, // position of the eye
centerX, centerY, centerZ, // position of the reference point
upX, upY, upZ); // direction of the up vector
`eye = (0, 0, 1)`
`eye = (0, -0.5, 1)`
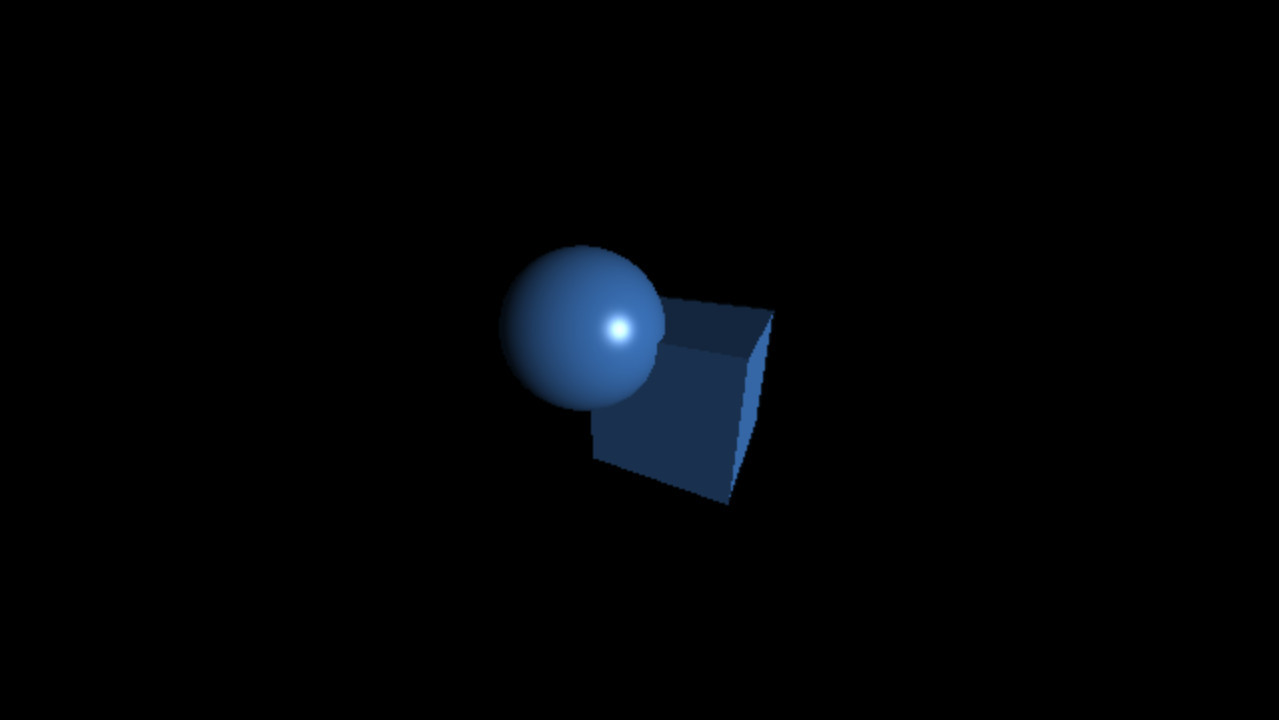
`eye = (0.5, -0.5, 1)`
Camera
Projection: perspective / modèle sténopé, `x_c = f_x (x_w / z_w)`
Code Processing
perspective(fov, // vertical field of view
aspect, // WIDTH / HEIGHT ratio
zNear, // distance to the nearest clipping plane
zFar); // distance to the furthest clipping plane
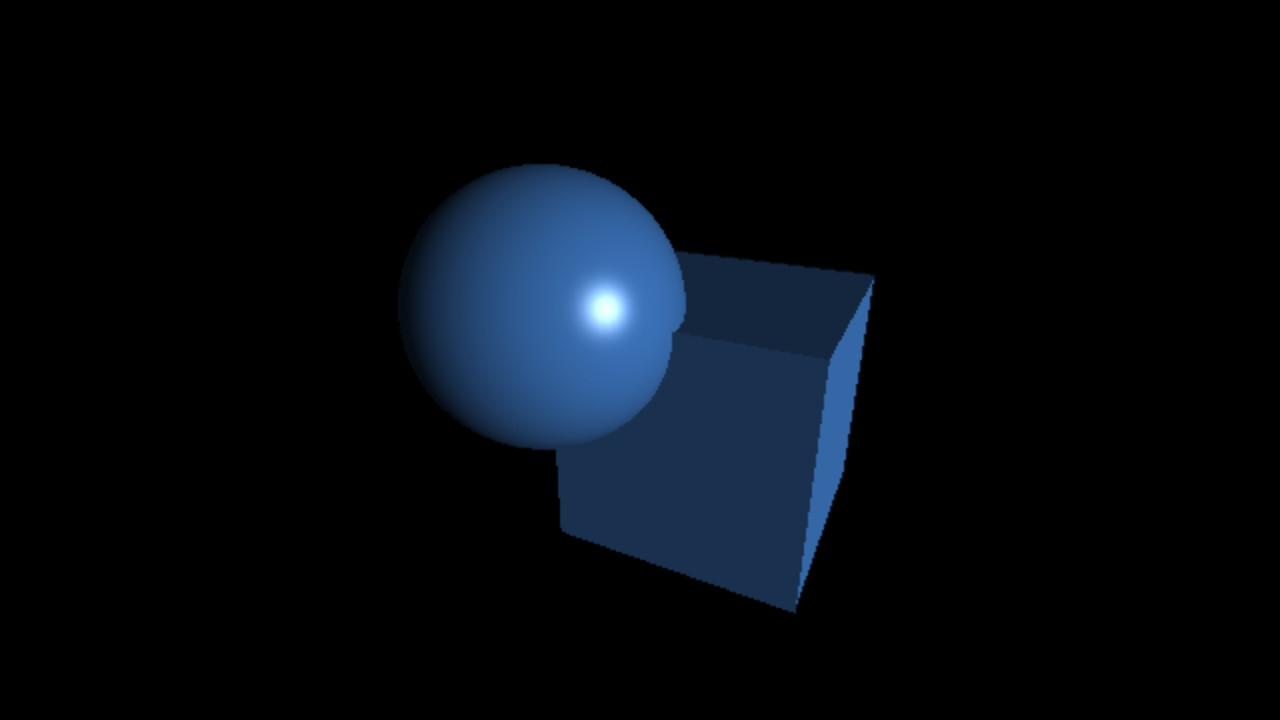
`fov = 60°`
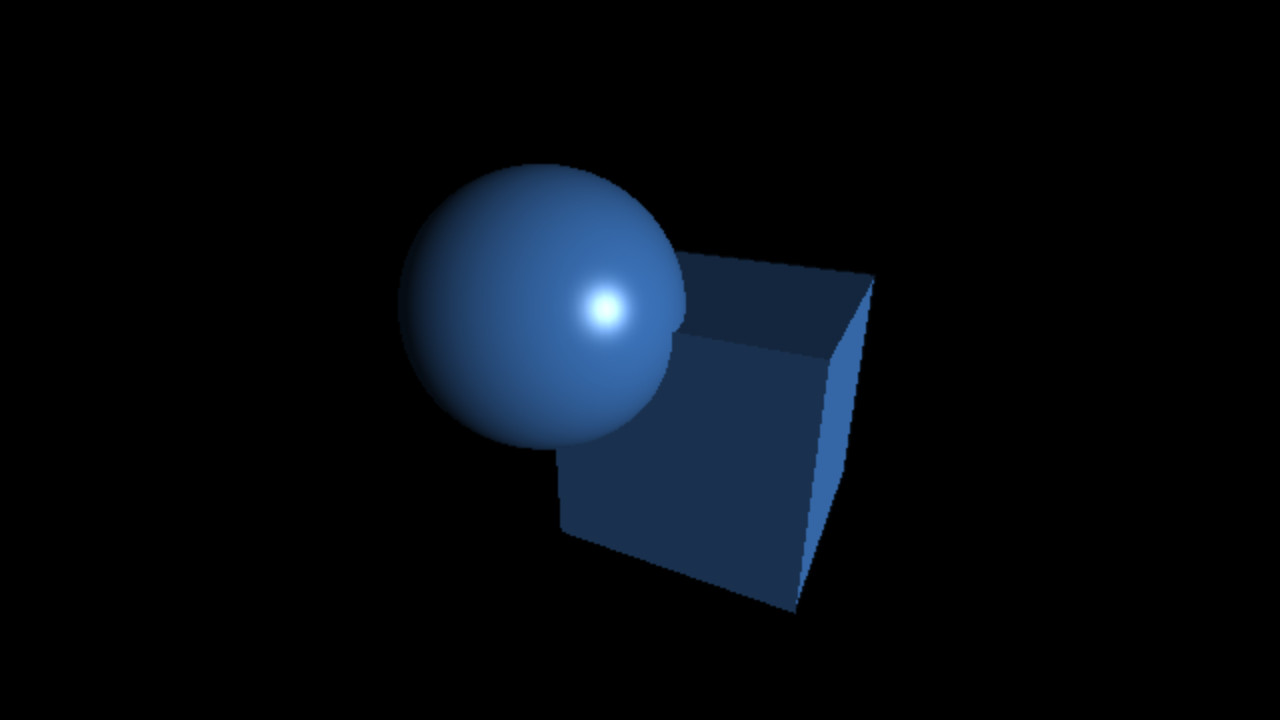
`fov = 30°`
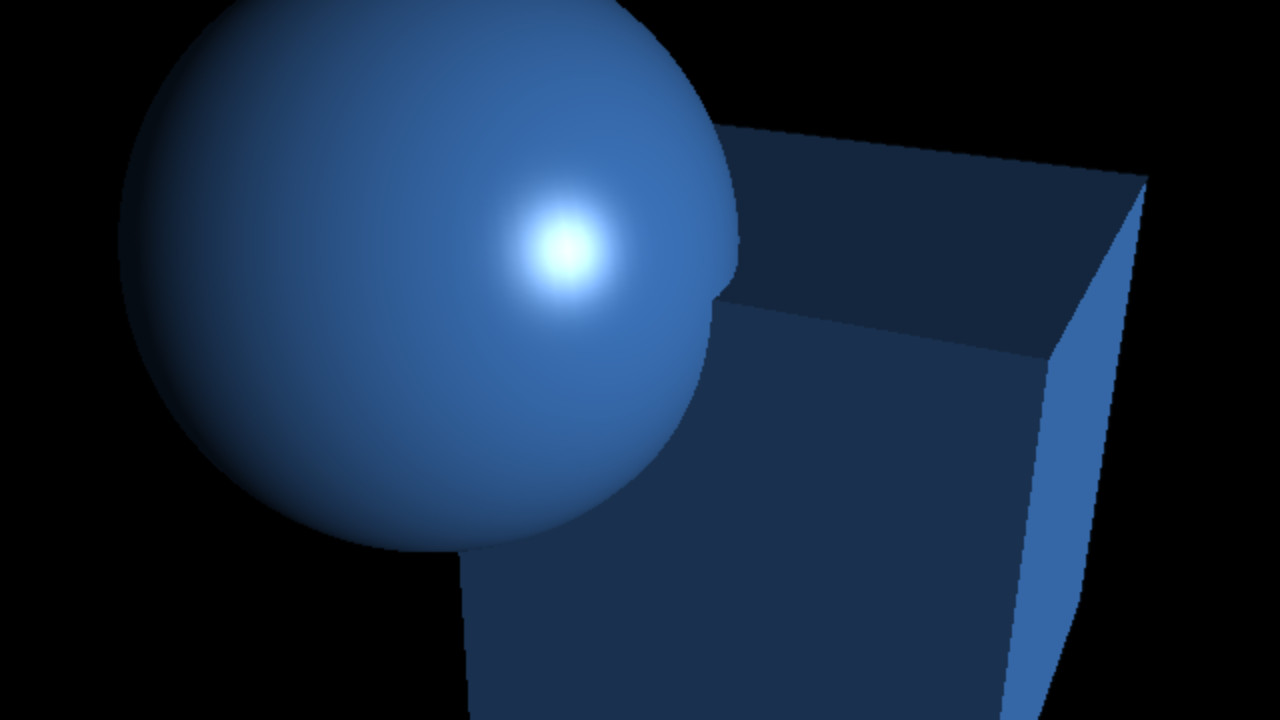
`fov = 90°`
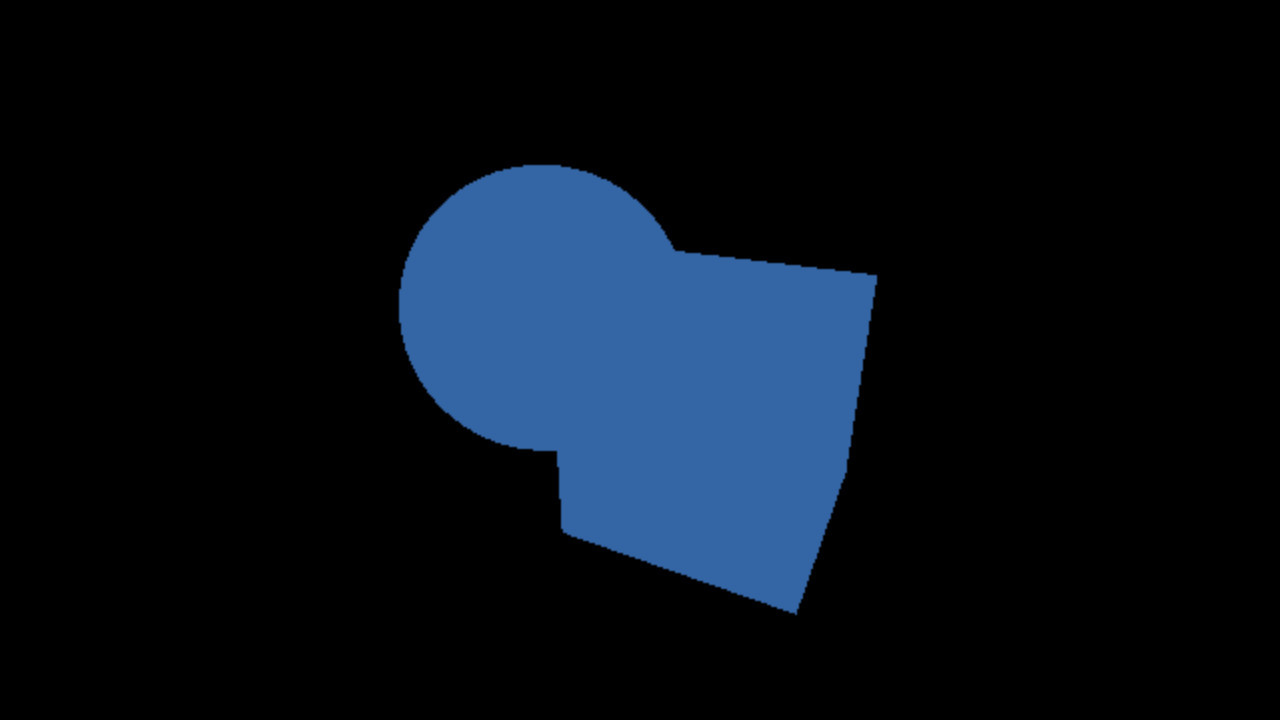
Géométrie
Prédéfinie
Code Processing
pushMatrix();
translate(0.125, 0.125, -0.125);
box(0.5, 0.5, 0.5);
popMatrix();
pushMatrix();
translate(-0.125, -0.125, 0.125);
sphereDetail(128);
sphere(0.25);
popMatrix();
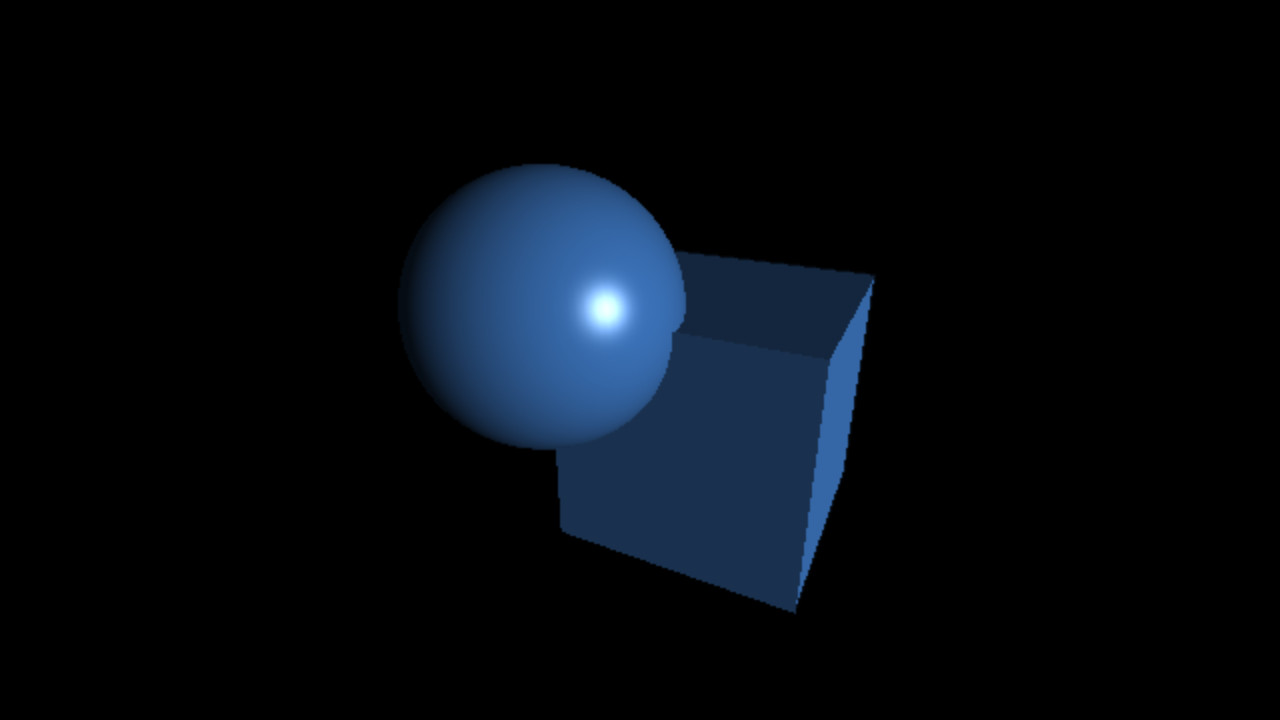
Géométrie
Définition explicite de géométrie: triangles, etc...
Code Processing
beginShape(TRIANGLES); // TRIANGLE_STRIP, POINTS, LINES, ...
// +z face of a cube: 2 triangles
vertex(-0.25, -0.25, 0.25);
vertex( 0.25, -0.25, 0.25);
vertex( 0.25, 0.25, 0.25);
vertex(-0.25, -0.25, 0.25);
vertex( 0.25, 0.25, 0.25);
vertex(-0.25, 0.25, 0.25);
// ...
endShape();
Matériaux et illumination
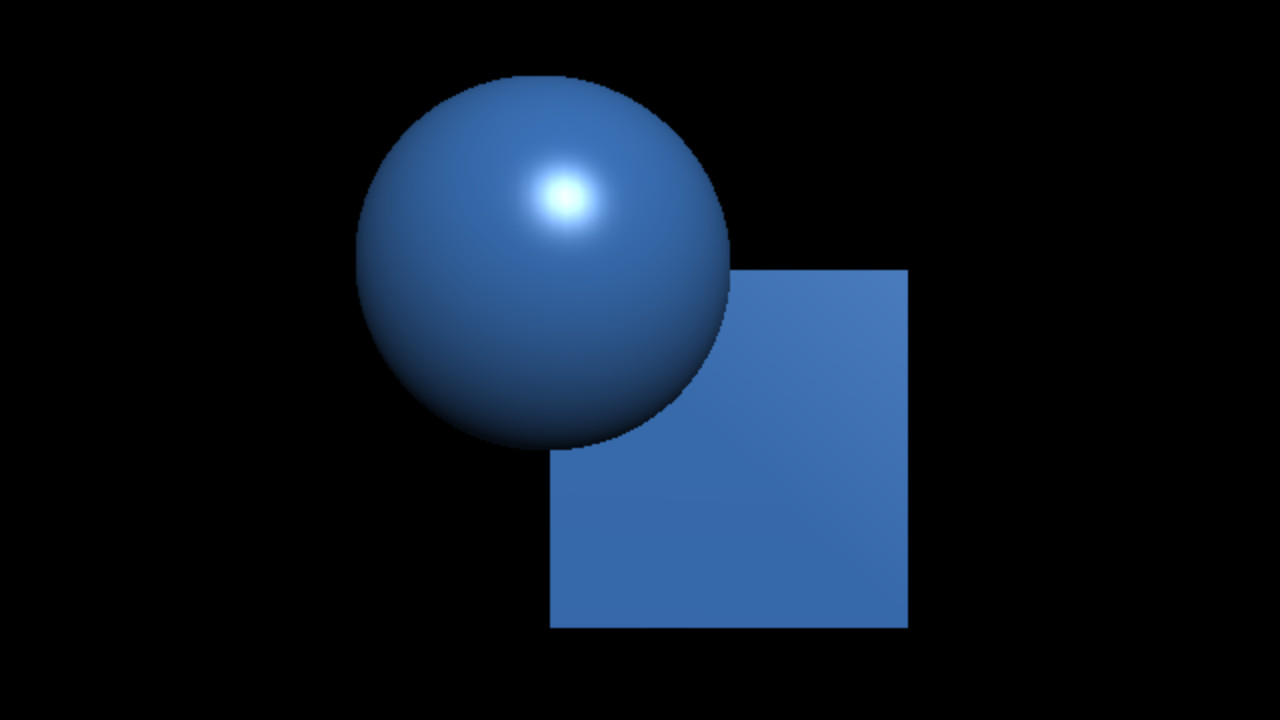
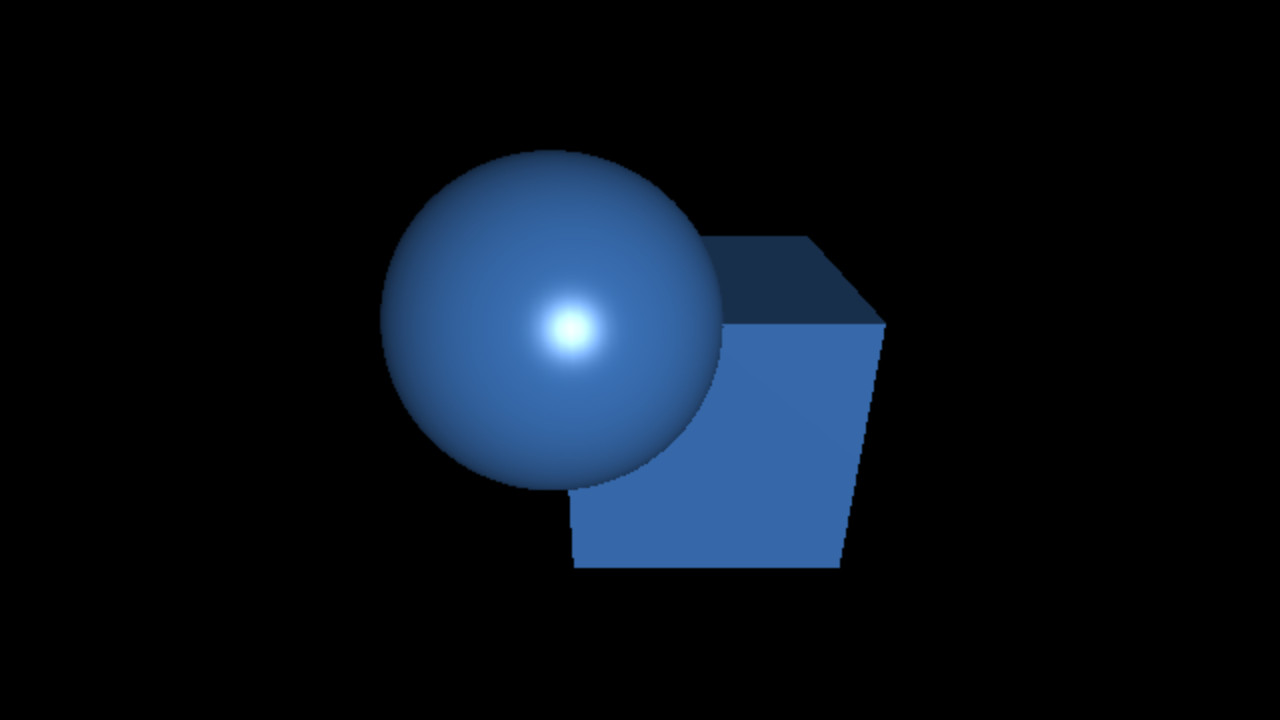
Sans illumination (couleur constante):

Avec illumination:

Avec illumination (matériau + lumière):

- Matériaux: propriétés des surfaces de la scène
- Sources de lumière: directionnelle, ponctuelle, etc...
Matériaux et illumination
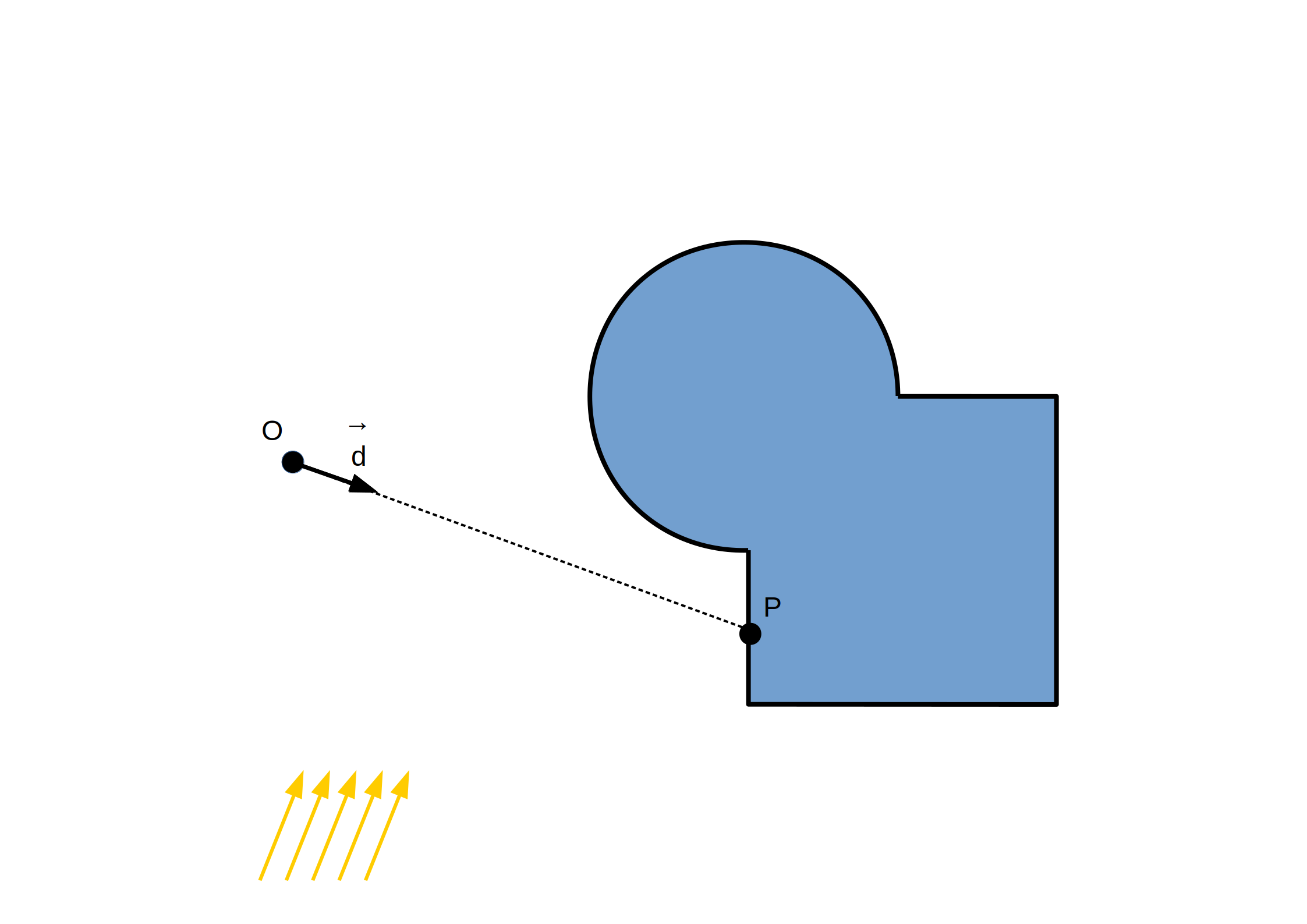
Formules empiriques de calcul d'illumination locale
(modèle de Phong):
`C = C_(ambient) + C_(di f fuse) + C_(specu lar)`
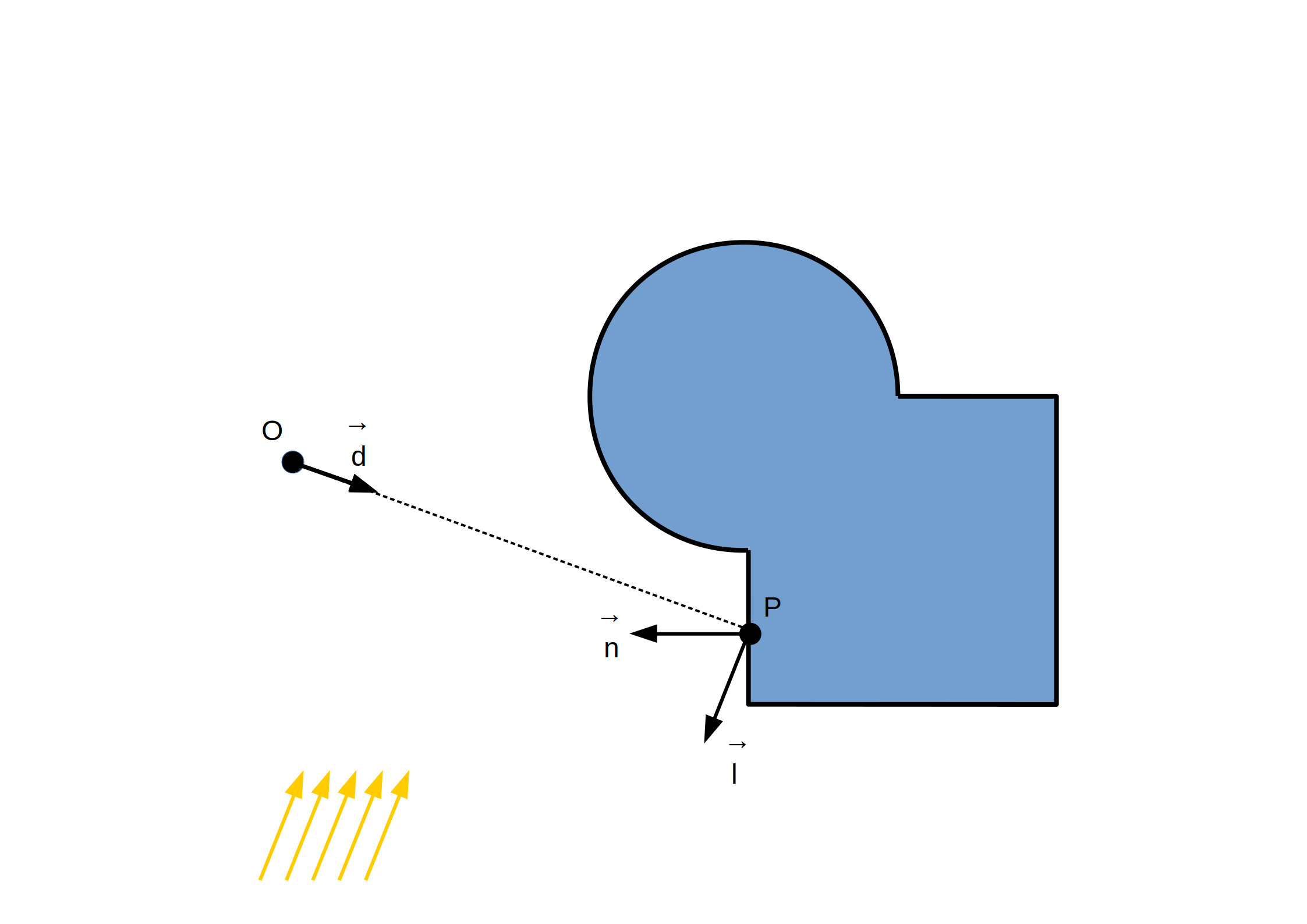
`C_(ambient) = L_(ambient) M_(ambient)`
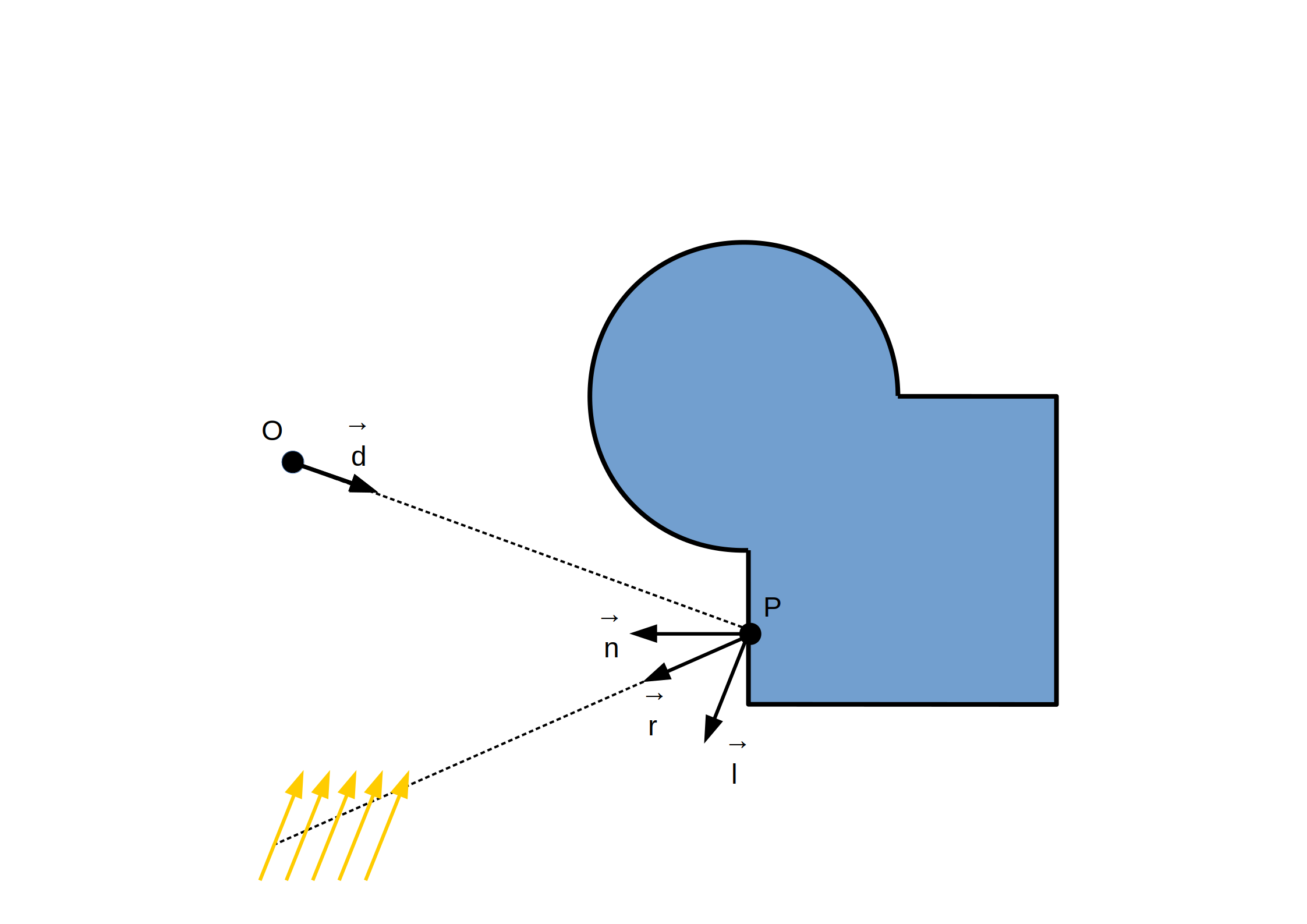
`C_(di f fuse) = L_(di f fuse) M_(di f fuse) max(< vec n . vec l >, 0)`
`C_(specu lar) = L_(specu lar) M_(specu lar) max(< vec r . vec l >, 0)^(shi ni n ess)`
Matériaux et illumination
Matériaux et illumination
`C = C_(ambient)`

`C_(ambient) = L_(ambient) M_(ambient)`
Code Processing
ambientLight(31, 31, 31);
Matériaux et illumination
`C = C_(ambient) + C_(di f fuse)`
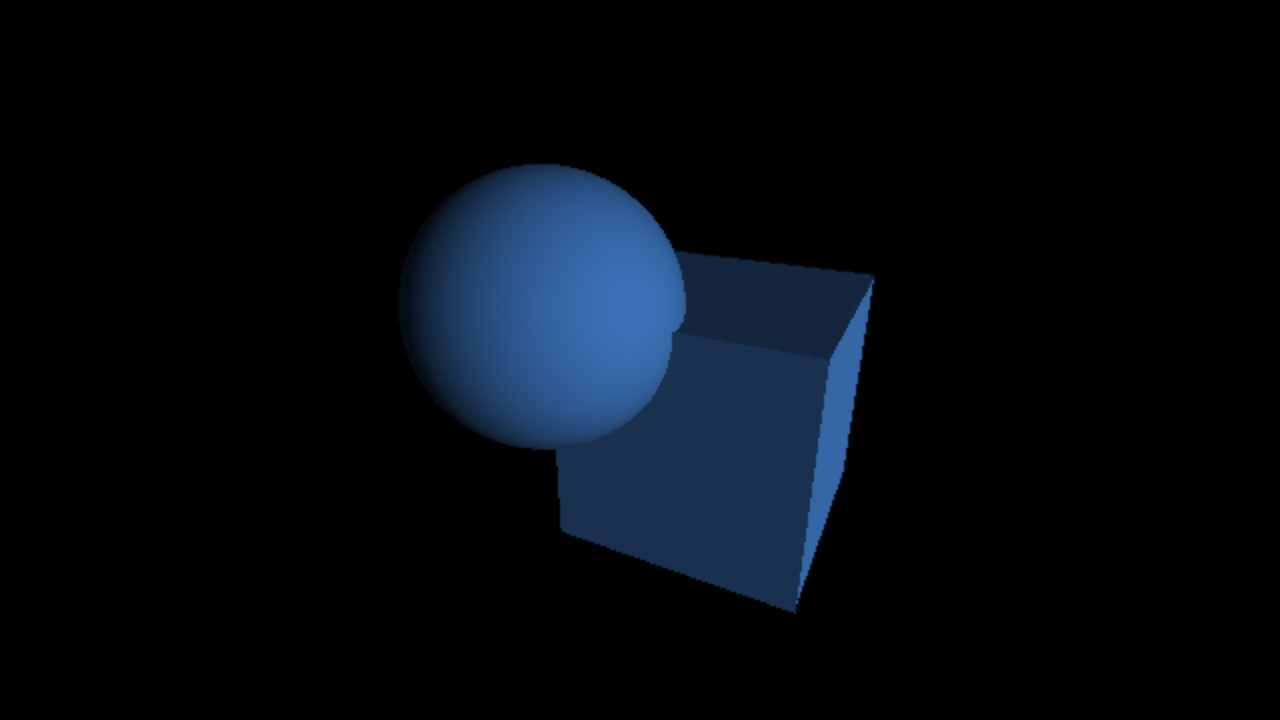
`C_(di f fuse) = L_(di f fuse) M_(di f fuse) max(< vec n . vec l >, 0)`
Code Processing
ambientLight(31, 31, 31);
directionalLight(255, 255, 255, -0.5, 0.75, -2.0);
fill(52, 101, 164);
Matériaux et illumination
`C = C_(ambient) + C_(di f fuse) + C_(specu lar)`
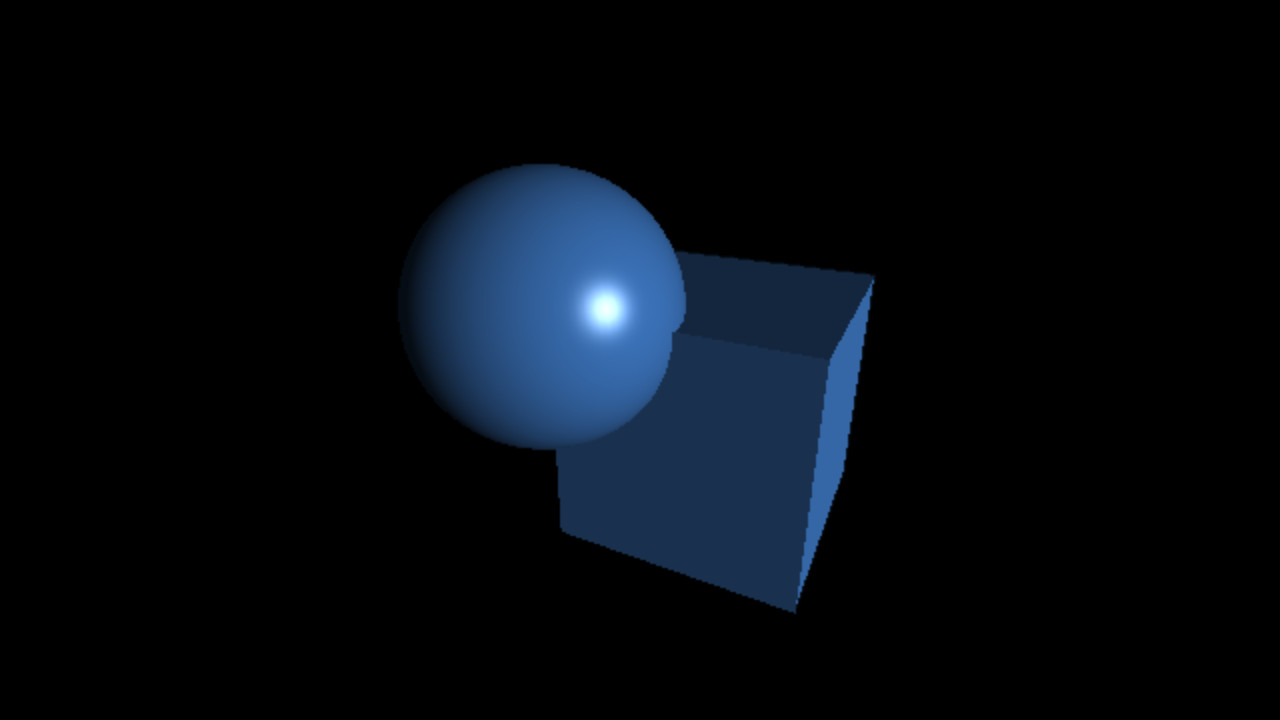
`C_(specu lar) = L_(specu lar) M_(specu lar) max(< vec r . vec l >, 0)^(shi ni n ess)`
Code Processing
ambientLight(31, 31, 31);
directionalLight(255, 255, 255, -0.5, 0.75, -2.0);
lightSpecular(255, 255, 255);
fill(52, 101, 164);
specular(191, 191, 191);
shininess(100.0);
Matériaux et illumination
`C_(specu lar) = L_(specu lar) M_(specu lar) max(< vec r . vec l >, 0)^(shi ni n ess)`
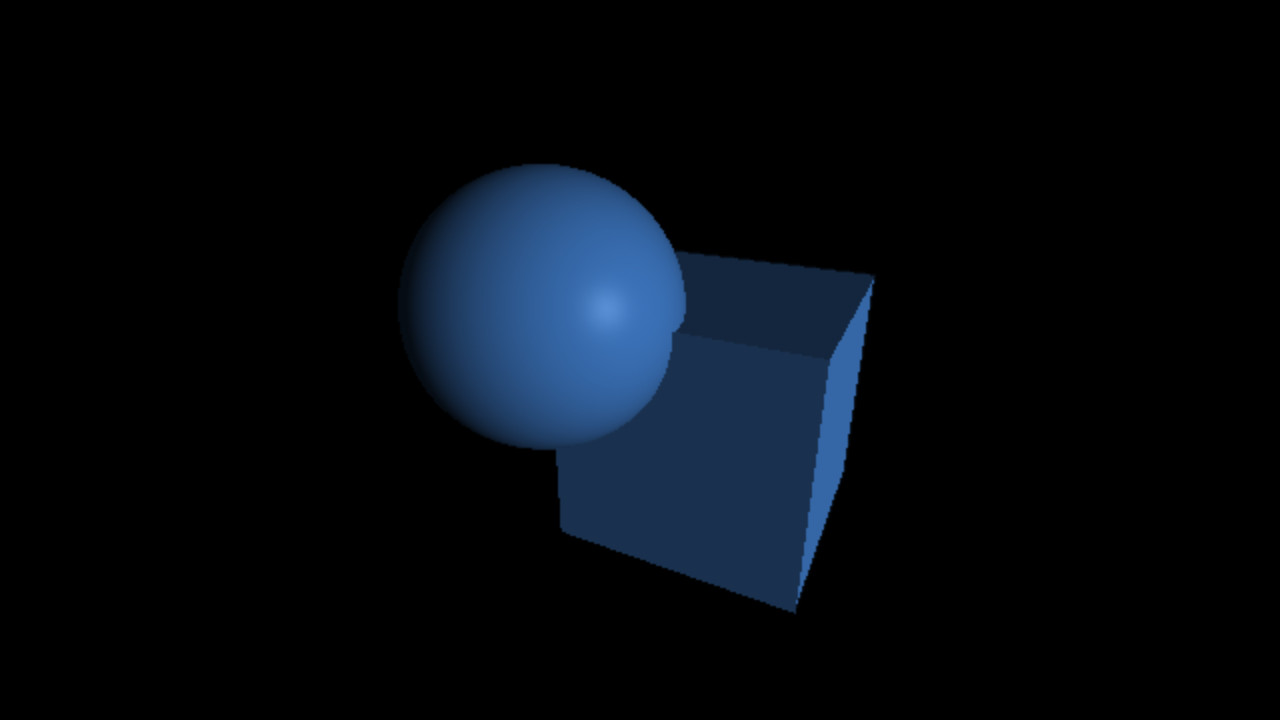
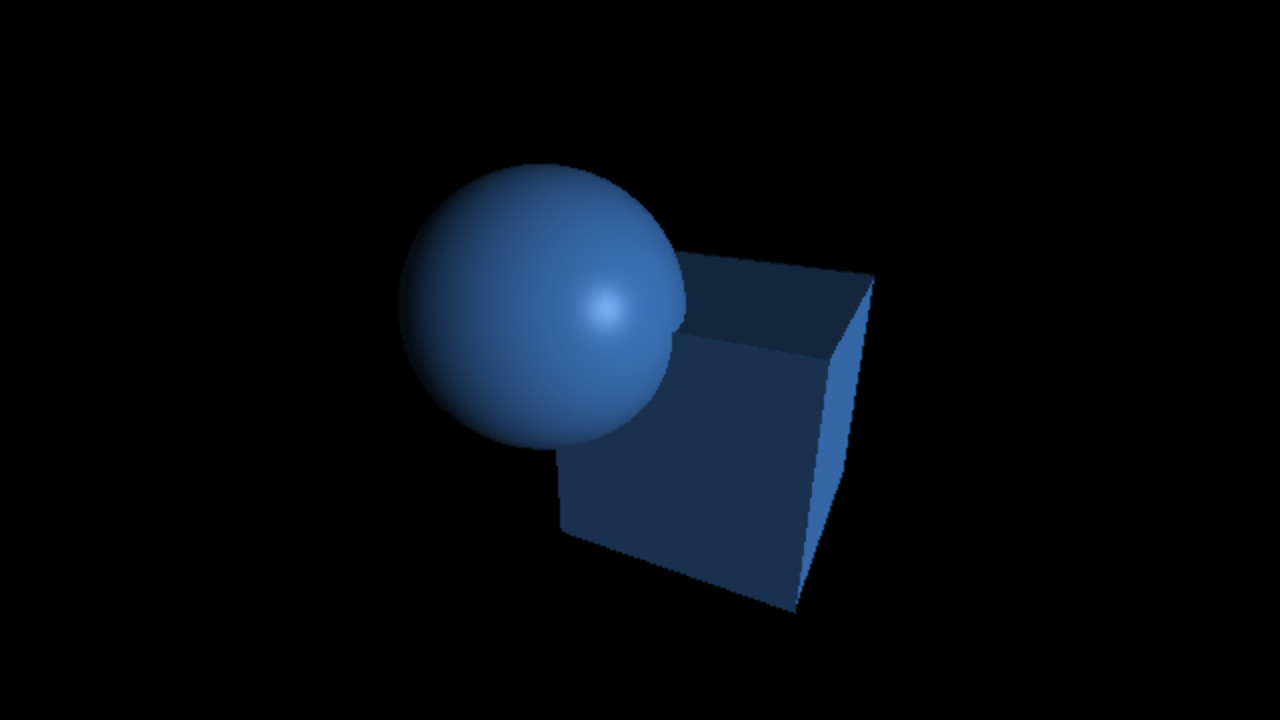
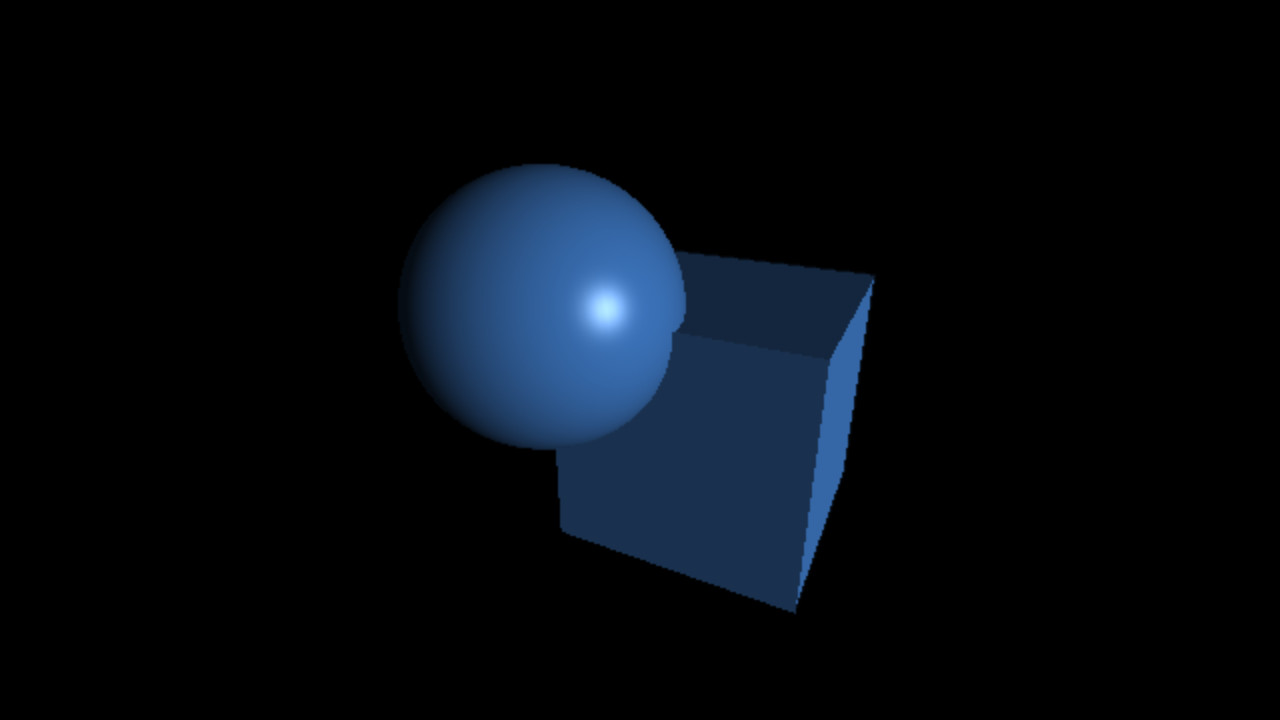
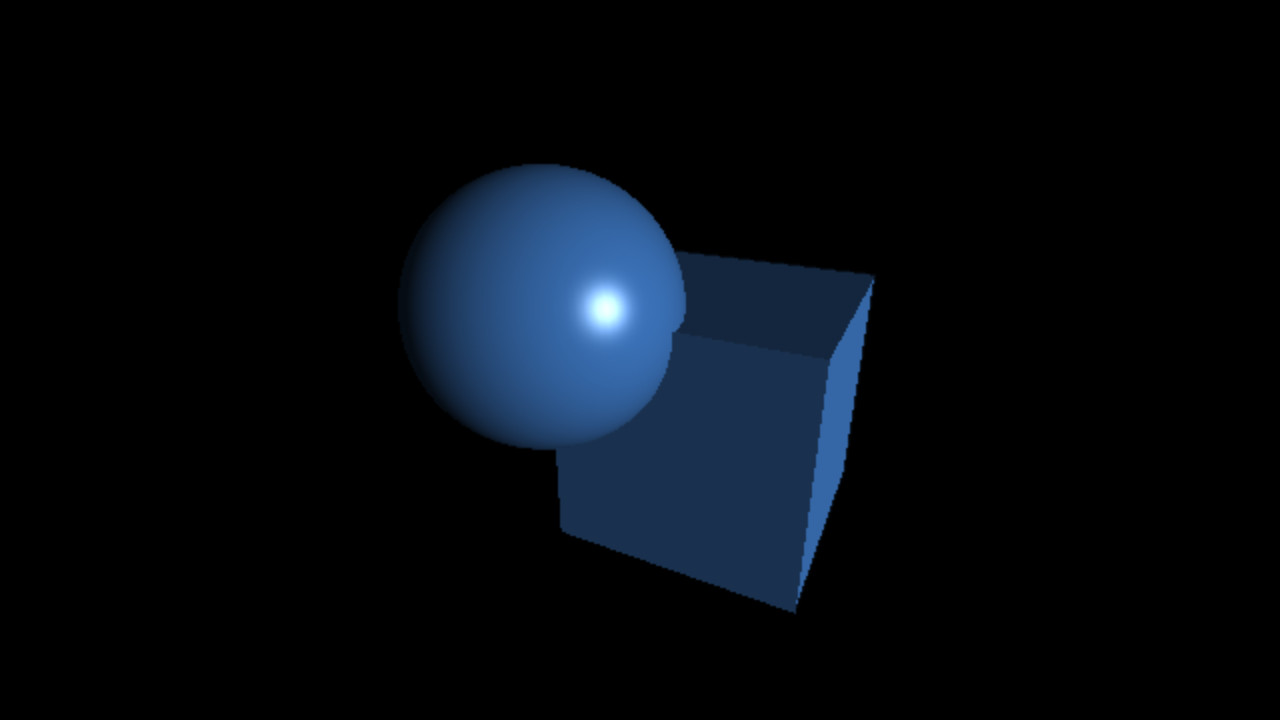
`M_(specu lar) = 12%, 25%, 50%, 75%`
Matériaux et illumination
`C_(specu lar) = L_(specu lar) M_(specu lar) max(< vec r . vec l >, 0)^(shi ni n ess)`
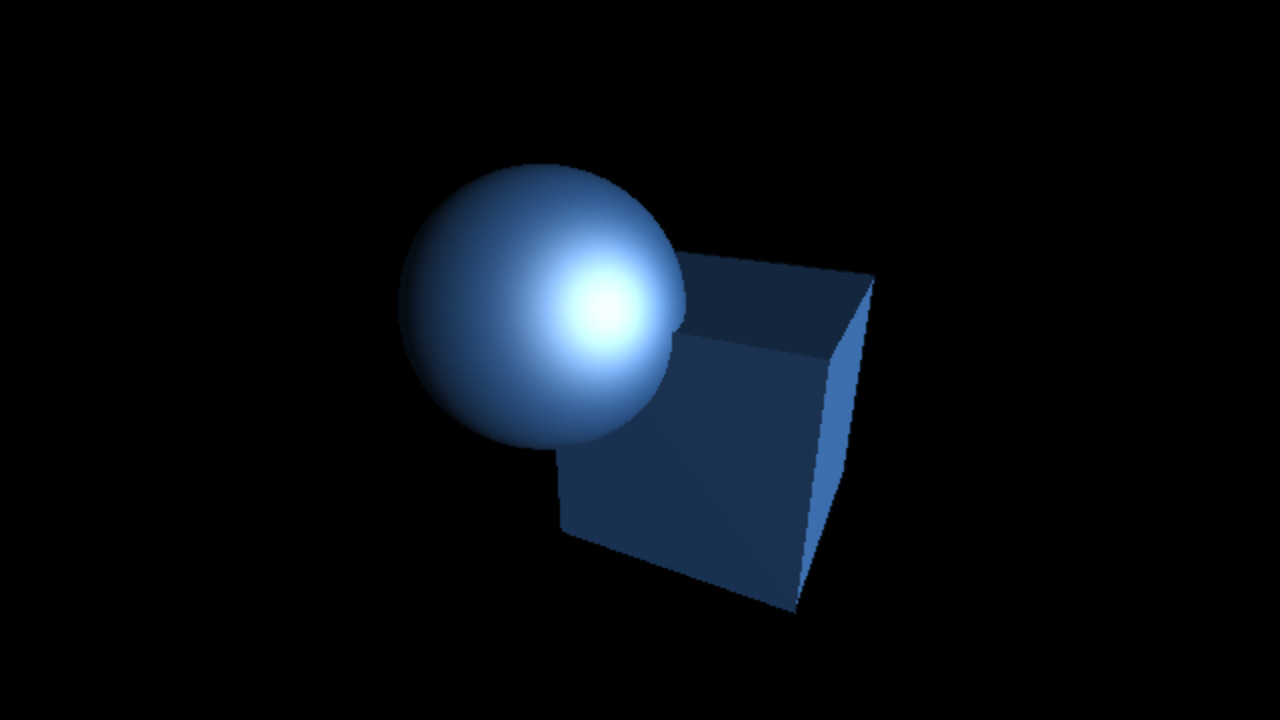
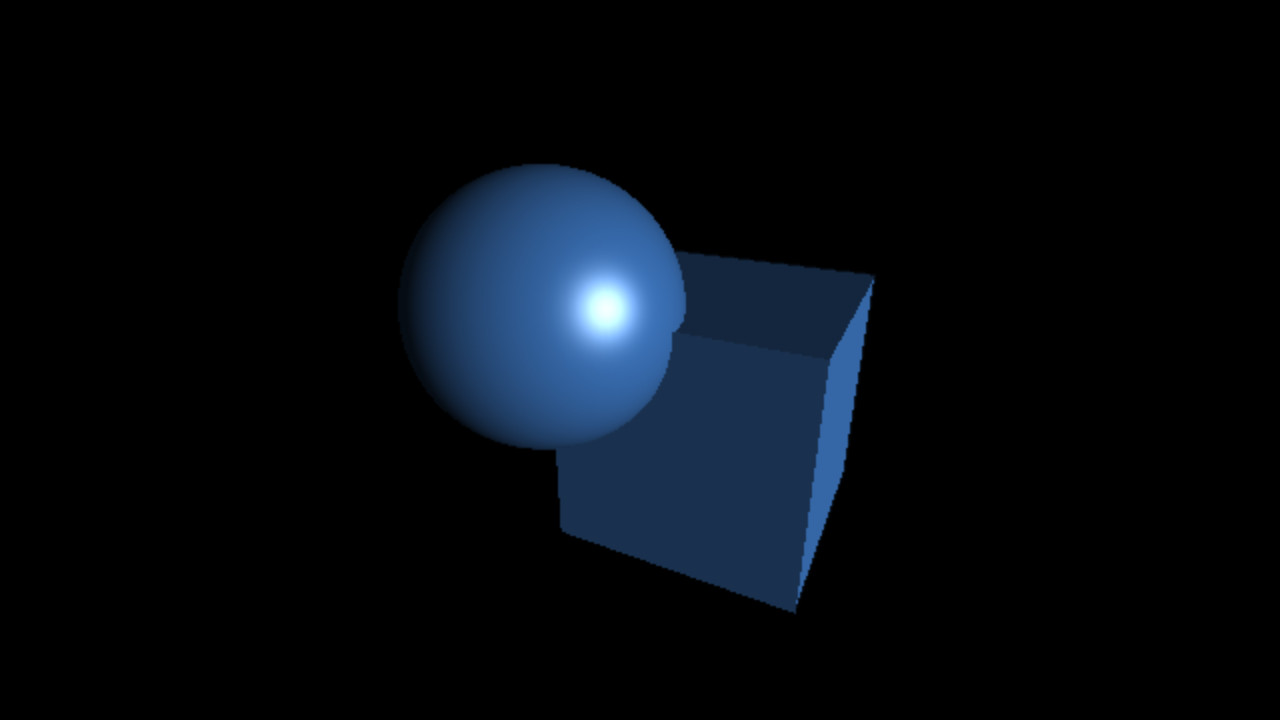
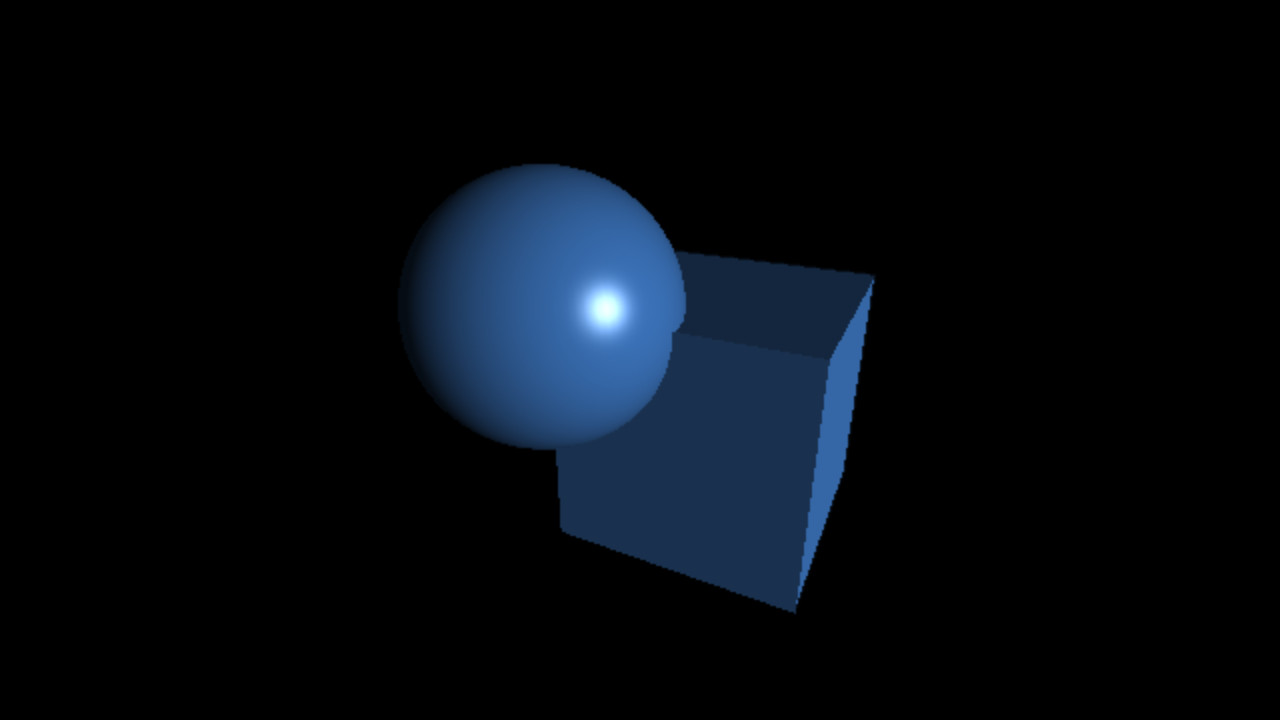
`shi ni n ess = 10, 50, 100`